What is Manufacturing Process?
Manufacturing process is a step-by-step procedure to convert raw materials into finished products with the help of machinery, labour, tools and equipment. Some products may also require chemical processing to change their properties and composition. A typical manufacturing or production line involves cutting, forming, machining and assembly, with in-process quality control.
The main objective of manufacturing is to produce quality goods efficiently and cost-effectively in order to meet customer demand. A business selects the production process based on multiple factors, including product design, production volume, production cost, quality requirements, availability of raw materials and resources, among others.
For example, if you have particular raw material in bulk and you use it to make finished goods in bulk or produce smaller batches to fulfill the customer orders without spending money on additional storage.
Also Read :10 Manufacturing ERP Modules You should look for in an ERP System
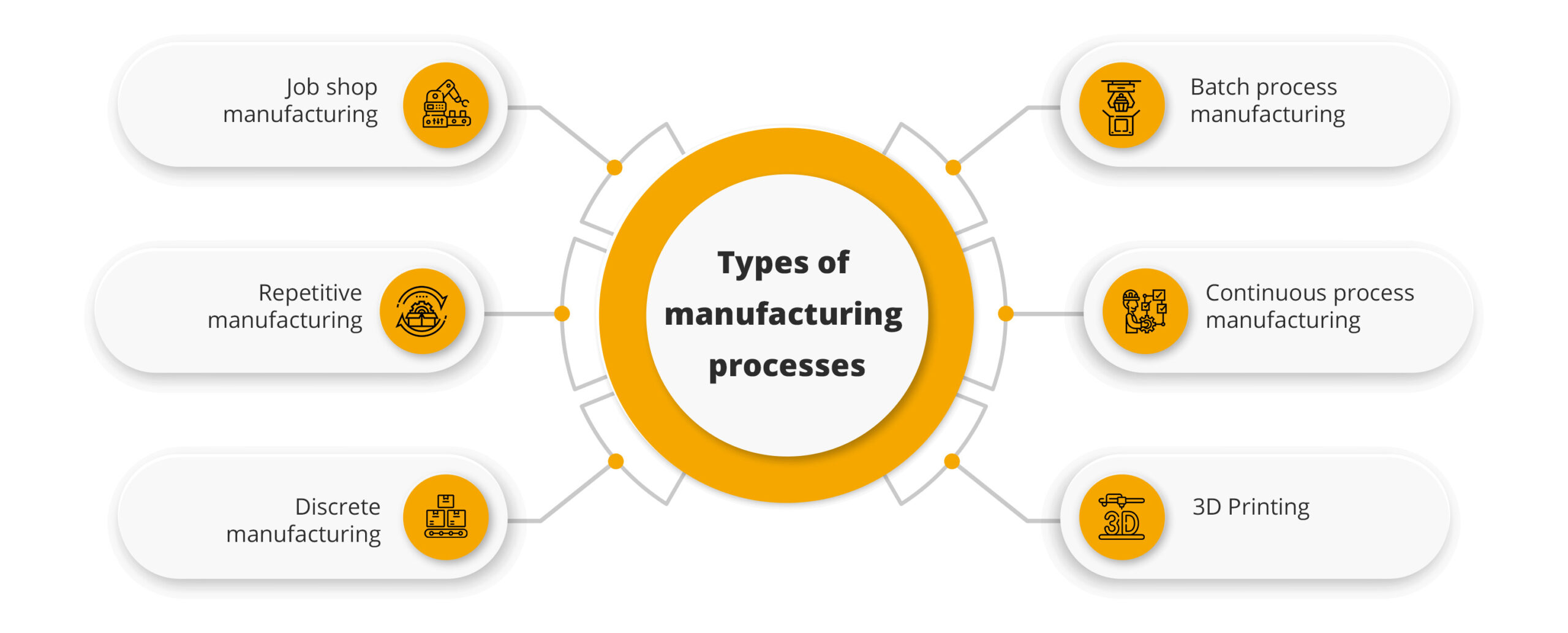
6 Types of Manufacturing Processes
Manufacturing processes can be broadly classified into six categories, namely, job shop manufacturing, repetitive manufacturing, discrete manufacturing, batch manufacturing, continuous process manufacturing and 3D printing. Let us explore every manufacturing process along with its advantages.
1. Job shop manufacturing
Job shop manufacturing is a manufacturing process to produce customized goods in small batches using skilled labor. It is often used in make-to-order manufacturing technique. Instead of a continuous assembly line, this method involves multiple workstations where every machine operator and worker individually adds value to the product before forwarding it to the next workstation. This approach is best suitable for custom manufacturing as it is a slower process
For example, if a business builds a custom wardrobe. It goes to each workstation for different processes, one will be sawing the lumber, another will be applying resin, the other will be designing it, and one will be polishing and varnishing it, and so on. The process continues till the product is ready.
- Advantage : Job shop manufacturing type Offers high flexibility to produce customized products. Process can be frequently modified at a relatively low setup cost to meet the technical specifications of multiple customers.
2. Repetitive manufacturing
Repetitive manufacturing is a continuous manufacturing process, especially used in make-to-stock scenarios, for producing similar products in high volume. Due to bare minimum product variations, the assembly line runs repetitively without needing many changes. Automated machinery and robots are frequently deployed here to increase output and efficiency.
A manufacturer relies on repetitive manufacturing to repeat the same process on the assembly line. This approach continuously repeats the manufacturing process 24*7 for all similar products with faster operation speeds.
Some of the industries that use repetitive manufacturing processes are electronics, automotive, semiconductor, and consumer durables. For example, it is common for car manufacturers to use sales forecasting for mass production or repetitive manufacturing of high-demand car models.
- Advantage : Good for mass production with highly standardized processes. Easy to reach economies of scale, which help reduce per-unit cost.
3. Discrete manufacturing
Discrete manufacturing is a manufacturing process where the end product is individual, countable product such as car, smartphone, etc. It is a flexible version of repetitive manufacturing, where we make frequent changes in assembly line to make diverse products. A configuration change in assembly is called a changeover, which affects cost of production.
In discrete manufacturing, especially for products like computers and laptops, frequent customizations require adaptable assembly lines. ERP for electronics manufacturing efficiently manages these changes, ensuring production agility while meeting quality standards and customer demands.
- Advantage : Variation in assembly and sub-assembly lines gives flexibility to produce customized products to cater to specific customer requirements
4. Batch process manufacturing
Batch manufacturing is a production method where products are made in specified quantities or batches. Here, the full batch is processed together on a workstation before moving it to the next workstation. It is suitable when manufacturers require flexibility in product variety and mass production is not needed. Industries that commonly use batch manufacturing processes are food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, furniture and chemicals.
- Advantage : Because products are made in batches, it enables high traceability and quality control of specific batches. Moderate customizations can be made cost-effectively without making significant changes to the assembly line.
5. Continuous process manufacturing
Continuous process manufacturing, also called flow production, is a manufacturing process where products are manufactured nonstop without any manual interruptions to the assembly line. It is similar to repetitive manufacturing as it involves high-volume production of goods. However, the raw materials used in continuous manufacturing primarily include gases, powders, slurries and liquids, instead of solid constituents used in repetitive manufacturing.
Some of the industries that use continuous process manufacturing are pharmaceuticals, power stations, chemicals, fertilizers, and furnaces.
- Advantage : Enables cost-effective production on a large scale. The production flow can go on 24X7 with minimum downtime, which improves resource utilization.
6. 3D Printing
3D Printing, also called additive manufacturing, is an advanced manufacturing process that utilizes digital three-dimensional models and CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software to easily manufacture complex products. In contrast to traditional models of manufacturing, where we remove material from large blocks through cutting and machining, additive manufacturing adds material layer by layer to construct a product.
A wide variety of products today are manufactured using 3D printing, such as industrial parts, shoes, prosthetic limbs, medical and dental devices, and more.
- Advantage : Supports on-demand production of goods. Complex geometric designs can be made quickly with relative ease. Ensures minimal waste as the material is only added when needed.
Types of Manufacturing Techniques
1. Make to Stock (MTS)
Make to Stock, also known as push strategy, is a production technique to produce goods in advance based on demand forecasting and store them as inventory. This strategy helps reach economies of scale and enables faster order fulfillment when the customer order is received. MTS is common in the retail and FMCG industry.
2. Make to Order (MTO)
Make to Order, also called pull strategy, is a production technique where goods are only produced after the customer places the order, minimizing inventory storage costs. Businesses use this strategy for manufacturing complex products requiring high customization. Because MTO is demand-driven, lead time for customers is higher.
3. Make to Assemble (MTA)
Make to Assemble is a hybrid approach to manufacturing where standard components are pre-manufactured and stored so that they can be used along with custom-built components for final assembly. As MTA is a mix of MTS and MTO, it allows businesses to offer moderate amount of customization to customers. Also, the lead time here is relatively lower than MTO.
Steps of the Manufacturing Process
It is vital to know the steps or the stages of the manufacturing process for certain manufacturing processes and industries.
1. Create a product vision
It is vital to have a product vision, brainstorm with your team and develop a vision as it is the seed that will grow into a successful product. Understand your target audience, market size, the demand for the product, competitors, trends, funding requirements, and product roadmap.
2. Research your product niche
Before investing in the vision, research and gather insights about your niche. Find information on how you can make your custom product stand out, or if you prefer contract manufacturing and the different ways to market your product.
3. Design the product
In this stage, keep the end user’s needs in mind and design the product. Analyse the resources required, the lifespan of the good, accessories and the function of the product.
4. Finalise the design
After figuring out all the answers in the earlier step, finalise the design of your product. Create a bill of materials for all the resources which you will be using for the manufacturing process or working prototype.
5. Test the prototype
In this stage, test the product and examine if it will serve the customer demand. In this stage find all the issues with the design and solve them.
6. Manufacture the product
Develop a manufacturing plan comprising the details of raw materials, parts, components and the stages of the assembly process.
7. Get reviews and do more testing
Before launching the product in the marketplace, do more testing and get feedback. This avoids failures.
8. Launch the product
After finishing all the above stages, start with the marketing campaigns and launch the product.
Also Read : India’s Top 12 Manufacturing ERP System in 2025
Choosing a Manufacturing Method
Industries are diverse and they have to rely on multiple manufacturing processes or dedicated production lines to successfully finish a product. One manufacturing process doesn’t fit all business types. So choosing a manufacturing technique depends on various factors discussed below :
- The raw materials usage
- Total budgeting
- The duration of each stage
- Product dimensions
- Product volume
- Available machinery and tools
- Wastage and dimensions of the goods.
Conclusion
The manufacturing industry is vast and a complex business sector. Manufacturing processes vary depending on the type of industry. Relying on any manufacturing software like an ERP system can ease the complex process and efficiently complete all the stages. Leveraging manufacturing systems will boost revenue, establish process control and helps in the growth of the business. It helps in staying relevant and competitive.
Types of Manufacturing Processes FAQs
1. What Are The 4 Main Types Of Manufacturing Processes?
The four main types of manufacturing process are job shop manufacturing, repetitive manufacturing, batch manufacturing and continuous process manufacturing. Job shop is suitable for small-scale, customized production while repetitive is ideal for large-scale standardized production. Batch manufacturing is suitable for processing small, custom batches. Continuous manufacturing is the 24/7 manufacturing, suited for high-volume production.
2. What Is Industry 4.0 And Why Is It Important For Manufacturing Processes?
Industry 4.0 or Fourth Industrial Revolution is the new era of manufacturing with smart, automated factories that operate with enhanced efficiency, transparency and productivity. These highly-connected smart factories are built on systems using the latest digital technologies such as cloud computing, AI, ML and IOT, to enable real-time data sharing across business functions.
3. What Is The Classification Of The Manufacturing Process?
Manufacturing processes can be broadly classified into six categories, namely, job shop manufacturing, repetitive manufacturing, discrete manufacturing, batch manufacturing, continuous process manufacturing and 3D printing.
4. Which are the Top Manufacturing Processes Industry?
Some of the top Manufacturing Processes Industry are Chemical, Pharma, Automotive , Food & Beverage, and glass Industry.