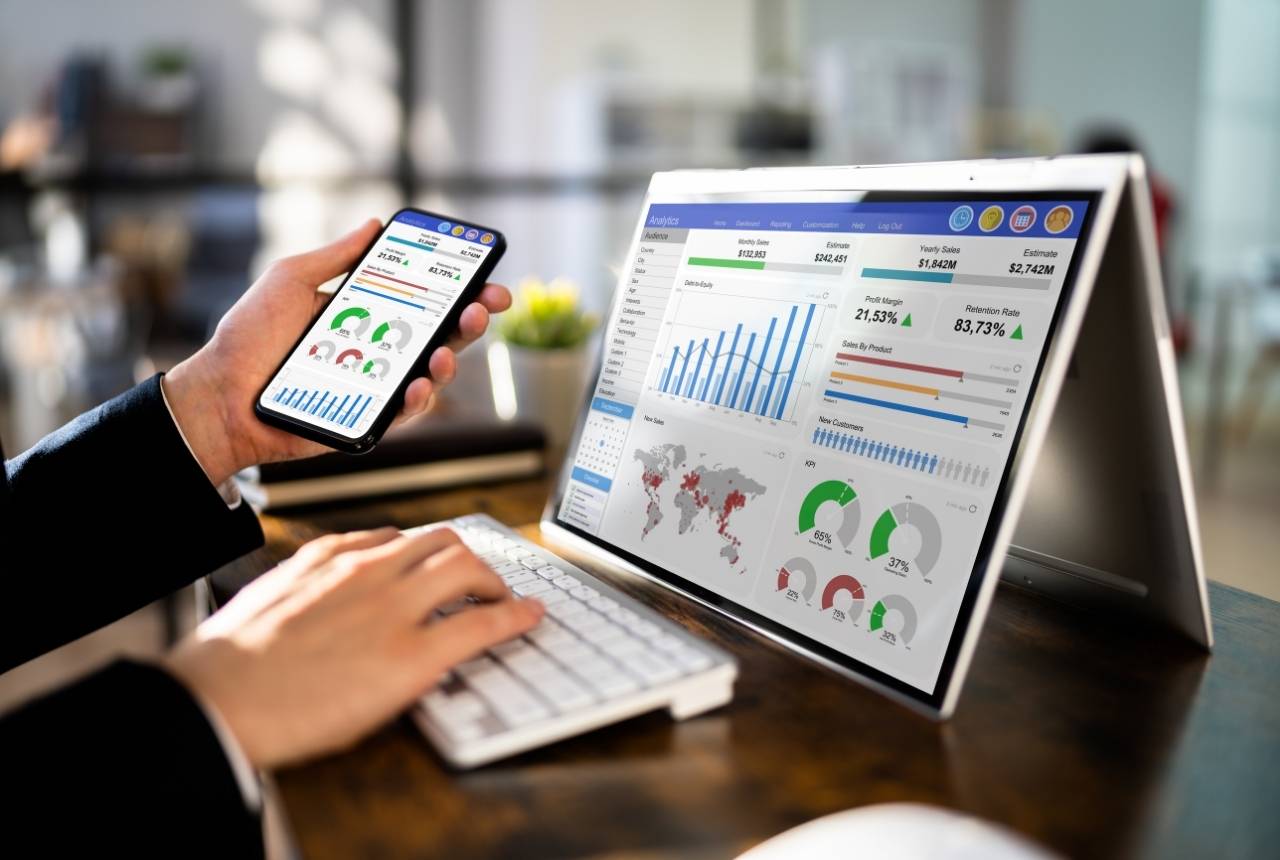
Business analytics is a statistical approach to solve real business problems and optimise operational performance by analysing and interpreting large datasets. The insights thus generated from this data are shared with the company’s stakeholders in an easy-to-understand format.
At its core, the business analytics process involves data analytics to identify trends, establish relationships between variables and predict business outcomes. To meet evolving customer expectations, businesses are increasingly adopting business analytics to improve their decisions.
Why Business Analytics is Important?
One of the key reasons why business analytics is becoming strategically important is the need to solve complex business problems. Every department generates a huge volume of data, but when that data is used to predict future outcomes, it delivers a new level of competitive edge.
To achieve this, business analysts use advanced, data-centric ERP software systems that enable them to perform statistical analysis and run predictive analytics models to gain actionable insights. The insights are then presented to key business executives for making informed business decisions.
What are the Benefits of Business Analytics?
Given the multifold benefits of business analytics, India Inc. is making business and data analytics solutions an integral part of their executive suite. It is interesting to note that the data analytics market in India is expected to grow at 35.8% annually from 2025 to 2030.
Let’s explore the various ways in which business analytics is beneficial for your business.
• Make decisions powered by data
Business analytics equips you with tools to identify patterns and solve issues. For example, before setting up a new product line, the production team can analyse how manufacturing software automation would reduce production costs while accounting for inventory and labour costs, and machinery output.
• Drive operational efficiency
To make supply chains leaner and more resilient to disruptions, business analytics facilitates demand planning to optimise resource allocation and adjust inventory levels. The operations team can even conduct an in-depth vendor analysis to set benchmarks for selecting new vendors.
• Recognise customer behaviour patterns
Business analytics powered by a modern ERP system allows you to segment customers, calculate customer lifetime value, and identify high-value prospects. The more closely you know your customers’ preferences, the more aligned your teams can be to offer suitable products and deals.
• Cut down risk factors
It’s no secret that successful businesses plan ahead for risks. Whether it is preventing equipment failures, liquidity crunch, or detecting fraudulent transactions, business analytics techniques like risk assessment modelling protect against risks through simulation and scenario planning.
• Plan budgets and predict revenue
Through predictive modelling, inputs like historical data on sales, seasonal and market trends, and customer behaviour can be analysed for forecasting demand shifts and revenue growth, crucial for making budgets. It can even predict how new tax regulations would impact your profits.
• Boost team performance
Business analytics enables companies to track key performance indicators of employees and pinpoint areas where time and resources can be saved. These data insights can be used to optimise processes by leveraging the wide-ranging benefits of ERP solutions and make employees more productive.
4 Types of Business Analytics
Business analytics can be classified into four main types, namely, descriptive analytics, diagnostic analytics, predictive analytics, and prescriptive analytics. These types primarily differ in what answers they provide. Descriptive analytics informs you about past performance, while diagnostic analytics highlights the reason behind it. In contrast, predictive analytics helps you predict potential outcomes, whereas prescriptive analytics recommends solutions to the issues.
1. Descriptive Analytics
One of the most commonly used techniques, descriptive analytics involves analysis of historical and current data to identify trends and establish correlations between variables. This technique provides information on what happened in the past and what’s happening at present.
For example, pharmaceutical companies frequently use descriptive analysis via their pharma ERP software to study past clinical trials for optimising dosage in future trials and improving patient safety.
2. Diagnostic Analytics
Diagnostic analytics takes business analytics one step ahead by figuring out why this outcome happened. This technique analyses data to identify the root cause of issues. Methods like diagnostic regression analysis and hypothesis testing are deployed to determine the cause of the outcome.
For example, when a manufacturer notices a difference between product demand in two markets, despite the same price, he uses diagnostic analytics to study factors like local competition and customer service.
3. Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics method is used to forecast future trends using historical data. Essentially, this technique plays a vital role in developing strategies and preparing for what is likely to come, either in the near or distant future. Often, regression and multiple regression analysis are used here.
For example, the finance team analyses customer payment records to detect delays and accounting errors, and makes next quarter’s cash flow projection for both best-case and worst-case scenarios. This information can even guide strategic decisions like automating the accounts receivable process.
4. Prescriptive Analytics
In prescriptive analytics, data is analysed to get advice on what to do next. This technique utilises machine learning algorithms to process a large volume of business data and obtain intelligent recommendations based on data analysis.
For example, before launching a new product, your product team feeds the ERP system with data on preferred product features, customer surveys, and competitors’ product features to get recommendations on what new features are likely to generate more revenue.
Components of Business Analytics
The components of business analytics refer to the various technical tools and methods that facilitate efficient data analysis. Here’s the list of components you should know about:
• Data Collection and Aggregation
Before analysis can begin, relevant data is collected, such as financial statements, transactions, and customer records. Data warehousing simplifies this process by centralising data in one location.
• Data Mining
Under data mining, the ERP application processes the collected data through techniques like data cleaning, sorting and clustering to uncover data patterns for cost reduction and profit maximisation.
• Association
This technique determines the relationship between two or more items in a dataset. Eg. a manufacturer may analyse customer buying patterns and discover which two items are often bought together.
• Text Mining
Here, unstructured textual data is processed and converted into a structured format. Text mining helps businesses identify relationships among texts and uncover hidden patterns to improve decisions.
• Forecasting
Forecasting uses historical data to predict future business outcomes. For example, past sales data can be analysed to forecast sales for the next quarter and reallocate resources to achieve sales targets.
• Optimisation
Optimisation is used to test business strategies through simulation. By comparing results, businesses can choose the best strategy. It is often used for optimising costs and improving business processes.
• Data Visualisation
This component is useful for representing complex data in suitable visual formats like colourful graphs and charts, so that it can be easily understood and acted upon by decision-makers.
Business Analytics Process
Follow these steps to be successful at business analytics within your organisation.
1. Establishing Objectives
Determine what you want to improve or what problem you want to solve. Then, decide what specific datasets you need to achieve that.
2. Data Collection
Next, go ahead with data collection from relevant sources. With the help of ERP integration, you can easily bring data from multiple systems to a common platform, saving your time and resources.
3. Data Cleaning
To make sure that your data is fit for analysis, datasets undergo cleaning to fill in missing data details. At this stage, even unwanted data like outliers are removed.
4. Data Analysis
Here, the data is analysed using statistical methods. The analysis must be flexible to allow you to test different combinations of variables while keeping your main objective in sight.
5. Outcome Prediction
Data analysis is followed by predictive modeling for forecasting business outcomes. As it enables ‘what-if scenario’ analysis to find the best possible solution, strategic business decisions emerge through this step.
6. Implementation and Monitoring
The selected solution is implemented and updated in the ERP database for future reference. Later, the decisions are analysed to understand their impact and return on investment.
Conclusion
As companies strive to stay competitive, business analytics tools offer the business intelligence needed to make faster, informed business decisions. Whether you are an established enterprise or a fast-growing company, business analytics is your weapon to predict outcomes and reduce future risks.
Sage X3 ERP has cutting-edge business analytics capabilities to analyse data from virtually any connected data source, eliminating the need for manual data mapping. Pre-built data models coupled with personalised dashboards and simplified user interface allow quick analysis and accurate reporting.
Business Analytics FAQs
1. What are the Four Pillars of Business Analytics?
The four pillars of business analytics are descriptive analytics, diagnostic analytics, predictive analytics and prescriptive analytics.
2. What are the Key Concepts of Business Analytics?
Business analytics involves selecting the right types of business analytics, deploying appropriate statistical models, and leveraging past and current data to predict and prepare for upcoming events.