What is considered a Fixed Asset in Accounting?
Summary: Assets are essential for a company to grow and generate revenue. Assets display the financial health of any organization. Plus, these assets are classified into many types like fixed assets when documented in the balance sheet. Each accounting period, its value is depreciated. Investors consider huge assets as a positive sign to invest.

Assets are resources owned by a company to execute business processes and aid in generating economic value for the business. Assets can be divided into two types – Fixed assets and current assets.
Current assets are a company’s resources that can be converted into cash within a year. Cash, cash equivalents, accounts receivable, stock or inventory, marketable securities, and prepaid expenses are some examples of fixed assets.
What is a Fixed Asset?
Fixed assets are resources a company uses for a long time to conduct business operations and generate revenue. Any business uses these fixed assets for more than one accounting period. Fixed assets cannot be sold immediately. They are used for many years, and each accounting period, the value of these assets is depreciated. Property, plant and equipment (PP&E) are a company’s fixed assets.
Fixed assets can be categorized into two types – Tangible assets and intangible assets. Tangible assets are physical assets that can be touched, such as buildings, land and equipment. Intangible assets are resources with no physical presence. For example, goodwill, trademarks, patents and licenses are Intangible assets.
<<Also Read: What is Fixed Asset ? | Meaning, Benefits and Examples>>
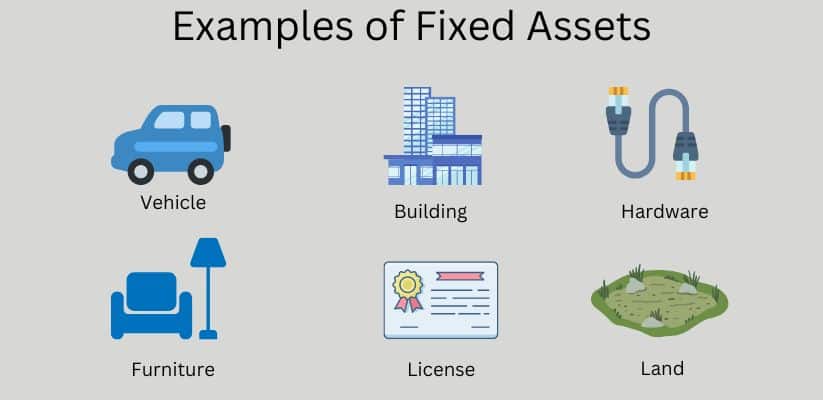
Example of Fixed Assets
I am listing some examples of fixed assets :
Tangible Assets
- Land
- Building
- Vehicles
- Computer hardware
- Industrial Machinery or equipment
- Furniture
- Office Supplies
Intangible Assets
- Software
- Copyrights
- Patent
- Goodwill
- License
Fixed Asset in Accounting
Fixed assets are purchased to perform business functions for the long term. These assets can deliver substantial economic value in the future.
Fixed Asset Accounting records all the financial activities from the purchase of the same to the disposal of the asset. It includes the record of the entire lifecycle of an asset – purchase, depreciation, audit, revaluation, impairment and disposal. Accounts for each fixed asset are maintained.
Accounting rules and regulations must be followed to maintain uniformity in a company’s financial statements. In India, the Institute of chartered accountants of India(ICAI) sets rules and regulations for accounting.
<<Also Read: Asset transfer from CWIP to Fixed Asset>>
Fixed Asset Accounting Cycle
Acquisition
The purchase of the fixed asset is documented on the balance sheet. It includes the total cost of the asset, shipment costs, and installation price recorded in the journal. Additionally, it accurately records if the fixed asset was purchased by paying the total price, instalments, or exchange.
Depreciation
Fixed assets are depreciated periodically. In the case tangible assets, its depreciated and intangible assets are amortized. All the accounting actions are documented in the ledger.
The standard methods used to depreciate fixed assets are the straight-line method, double declining balance, sum-of-the-years digits and units of production.
Revaluation
Revaluation of fixed assets is the increasing or decreasing value of investments compared to the market value.
Impairment
The period in which the market value of the fixed asset is lesser than the value recorded on the balance sheet. It is also known as writing down.
<<Also Read: The Scope of Financial Management >>
Disposition
After a fixed asset completes its useful lifecycle, it is disposed of by telling, trading or scrapping it. Simultaneously, these assets are eliminated from the accounting records. Finally, you can calculate the gain or loss of the asset you disposed during that particular accounting period.
What’s the Difference Between Total Assets and Net Assets?
A company has assets and liabilities. Companies accumulate assets normally to increase revenue. All the assets are registered on the balance sheet of a company. Net assets are the total value of assets a company owns, subtracting all the liabilities. Net assets are also referred to as net asset value. For an entity, net assets are pivotal because it gives vivid information on what a company owns and owes. Plus, it reflects the financial health of a company.
Net Assets calculation
Let’s look at the formula to calculate net assets.
Net Assets = Total Assets – Total Liabilities
Total Assets
Total are the assets owned by a company to procure economic value in the future. It includes cash, accounts receivable, inventory, equipment and many more. Companies own and acquire more assets to display financial strength and generate huge income in the future. Total Assets are divided into two categories – current assets and long-term assets.
Total Assets = Liabilities + Owner’s equity
Assets are significant for a company. There are many types of assets. All the assets together showcase the financial health of a company. If your company has more assets and fewer liabilities, it is a sign of yes for the investors. To grab a lot of projects, clients or investors, your company must display healthy finances.
In any firm, assets are documented on the balance sheet. It’s not easy to maintain all the records of fixed assets manually. There is a lot of software now that maintains, records and calculates the accurate value of all the assets for many accounting periods. They are also highly secured software. So it costs a lot to make an accounting mistake. Rely on the technology to get the best benefits for the good health of your company.




