What is a Sales Order?
A sales order is a formal document that binds the supplier to fulfil the customer’s order as per agreed terms. In other words, a sales order is an official confirmation for the buyer that the seller has accepted the order, which generally becomes a legally binding agreement once the buyer accepts it.
The supplier generates the sales order by including various details like product specifications, price, quantity, delivery date, and payment terms. To streamline the sales process, the entire order management is handled via ERP software, which seamlessly connects every department from sales to purchasing.
Why Are Sales Orders Important?
Sales orders are crucial for two main reasons. First, it is an official record for the customer that the supplier has accepted the order. Any order-related dispute that arises in the future can be addressed by referring to the sales order.
Second, it serves as an internal document for all the departments of the manufacturing company. Whether it is the sales team, production team, or the warehousing supervisor, everybody can track the sales order via the ERP solution and view order status throughout the supply chain.
Sales orders are even used for forecasting sales and analyzing customer orders to understand demand patterns. RBI data showed that during 2045-25, raw material and staff expenses increased by 6.6% and 10% respectively, for manufacturing companies, highlighting the growing need to automate the sales order process and mitigate the impact of rising costs on profits.
Components of Sales Order
A sales order includes many essential components that ensure clarity between seller and buyer. Some of the important details included are:
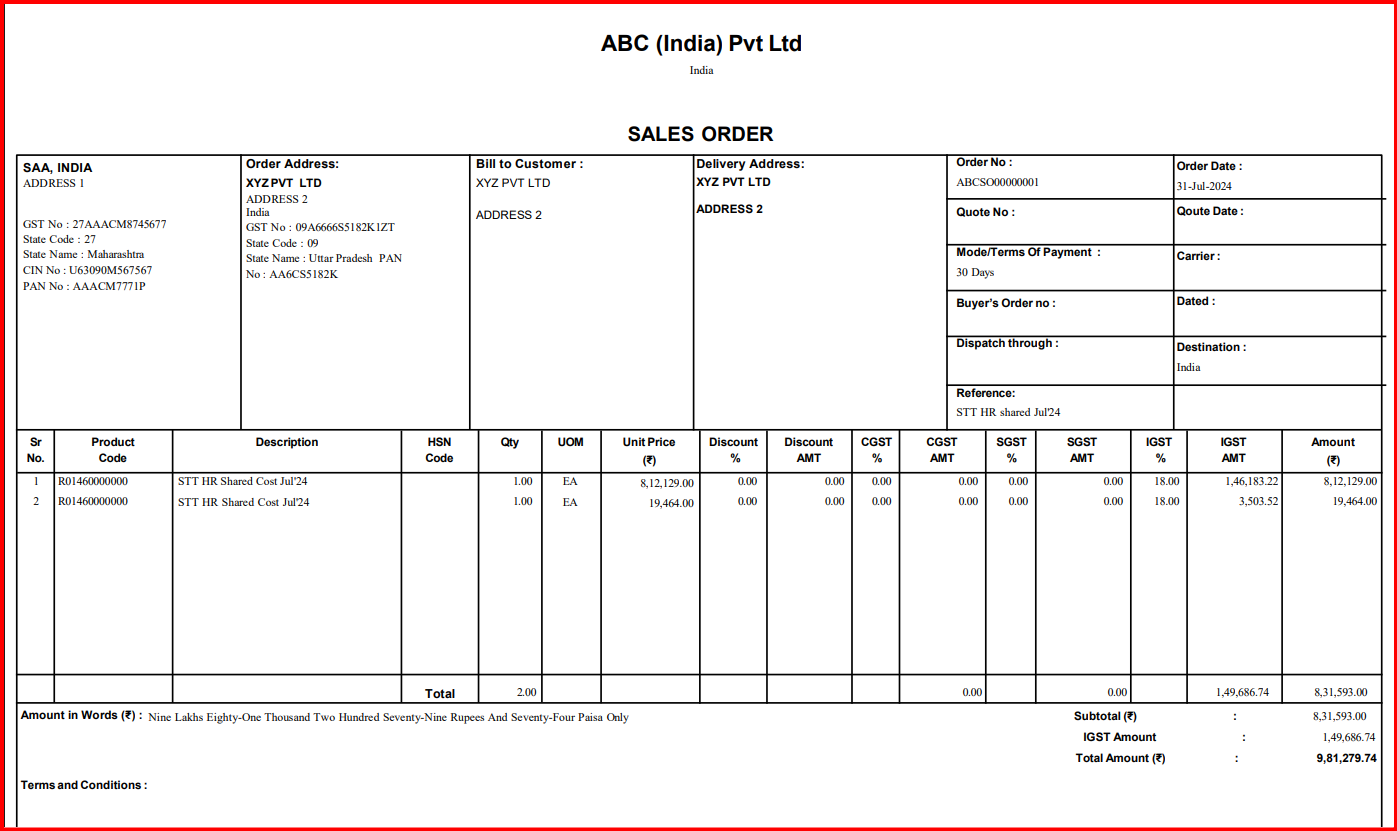
1. Customer Information – Customer name, billing address, contact information
2. Order Number – A unique order number generated using a sales management ERP system
3. Order Date – The date on which the sales order is generated
4. Product/Service Details – List of items/services, their specifications, quantity, and prices
5. Shipping Information – The delivery date and shipping address of the customer
6. Payment Terms – Preferred payment method, order due date, and tax applicable
7. Other Terms and Conditions – Mentions terms about order cancellation, if any (such as within 24-48 hours or before shipment) and return policies
Types of Sales Orders
→Cash Sales
In a cash sale, the customer places the order, pays for it, and the order is shipped. At other times, the customer pays during order pickup. As a consequence, the accounts receivable process is bypassed.
→Rush Order
This type of order is generated when a customer is in a hurry to get the order. The seller fulfils the order urgently. Unlike cash sales orders, payments for rush orders are made after the order is delivered.
→Scheduling Agreement
A scheduling agreement is a long-term agreement between the supplier and the customer, mentioning the product quantities to be shipped along with the order delivery date for each order. These are typically used for repeat orders.
→Third-party Sales Order
This option is utilized when neither the vendor nor the customer handles logistics. Instead, a third-party logistics service provider takes care of various services on behalf of vendors like warehousing, transportation, and returns management.
Sales Order Sample Format
Difference Between Sales Order and Invoice
Both sales order and sales invoice are issued by the vendor, but at different stages of the sales order process.
- A sales order serves as an internal document for vendors to track order status in the ERP software during the order fulfillment cycle. On the other hand, an invoice is a document to request payment from customers, besides serving as an official financial record of sale and purchase for both parties.
- The vendor generates a sales order to confirm the customer’s purchase request, beginning the fulfillment process, whereas an invoice is generated after the vendor fulfills the order.
Difference Between Sales Order and Purchase Order
The main difference between the two is that a sales order is issued by the seller while a purchase order is issued by the buyer.
- A sales order is used by sellers for internal order tracking; a purchase order is used by buyers for tracking their purchases. Also, sellers generate sales orders using the details in the purchase order.
- Sales orders can be modified when the negotiation between the two parties is ongoing. Once the buyer approves the final sales order, the order processing begins. On the other hand, purchase orders are not changed after issuing.
What are the Advantages of Sales Orders?
A sales order is a critical document during sales and offers several benefits to the vendor.
- Smoother Processes – Sales orders make the order fulfillment process accurate and error-free while offering end-to-end control from purchase order receipt to order delivery.
- Inventory Control – With product details and quantities mentioned in the sales order, the procurement and inventory teams can maintain adequate stock levels to facilitate smooth production and order fulfillment.
- Operational Efficiency – Since the data present in sales orders is integrated with other ERP functions, any changes made to the sales order are automatically updated, making the operations highly efficient.
- Cost Reduction – Another significant benefit is that it eliminates the need for multiple data entries across departments, reducing unnecessary clerical staff and the associated admin costs.
- Better Decisions – Sales orders help track order status, respond to customer queries faster, and improve operational and financial planning.
Sales Order Process and How ERP Manages It?
One of the primary objectives of ERP implementation is to automate order management, which brings operational efficiency, real-time insights, and maintains accurate records. Let’s explore the various steps of the sales order process and the role of an integrated ERP solution in managing it.
- Order InquiryThe sales process begins when the customer requests a quotation from the vendor. At this stage, the sales team uses the Configure, Price, and Quote (CPQ) process built into the ERP system to generate a quote.On receiving the initial quote, the customer may negotiate and settle on a new quote. That’s when the customer sends a purchase order (PO) to the vendor. The ERP uses electronic data exchange to automatically capture all the details in the PO.
- Order Validation On receiving the PO, the ERP validates the order by checking inventory levels, confirming the price, customer credit limit, ability to honour the delivery timeline, and other relevant business compliance rules.After the internal checks and validation are complete, the vendor creates a sales order via the software and sends it to the customer, signalling a final confirmation to the customer.Remember, if the vendor can’t fulfil the order currently because of inventory stock-outs or for any other reason, backorders can be created to fulfill the order at a later stage.
- Order ProcessingOnce the customer accepts the sales order, the manufacturing ERP software triggers all the upstream supply chain processes by checking existing inventory levels, generating a PO for purchasing new raw material, and beginning production and assembly.
- Order DeliveryWhen the finished goods are ready, they are sent to the warehouse for dispatch, or pickup by a 3PL company or by a transporter arranged by the customer. At this stage, the ERP system streamlines warehouse operations, supporting picking, sorting, and packing processes.
- Invoice Generation Finally, after the order is delivered, the system generates an invoice with a unique sales invoice number to request payment from the customer. The accounts receivable process begins at this stage.
- Returns ManagementIf the customer returns the shipment citing defects, damage, or order cancellation, the ERP system is capable of treating the inventory returns suitably and updating the billing with minimal manual intervention.
- Data AnalysisA significant advantage of using an ERP solution for order management is its advanced data analysis capabilities. It can analyze order-related metrics to track sales performance, identify issues, and improve order processing efficiency.
Conclusion
Sales orders are issued to confirm the buyer’s request for purchase. They include all the necessary details like product specification, quantity, and price, which serve as a reference for the manufacturer to process the order and maintain clear communication with the customer.
Sage X3 is a multi-functional ERP software helping businesses to overcome traditional limitations of order management. It can seamlessly collaborate with other departments and integrate with existing systems to help you fulfil orders on time and enhance the experience for your clients.
Sales Order FAQs
1. What Is Issued First, Sales Order Or Invoice?
In the sales process, a sales order is always issued before the invoice. Typically, a sales order is issued before order processing, whereas an invoice is issued after order delivery.
2. What Is The Role Of Sales Order?
A sales order is an official confirmation by the vendor indicating that they have accepted the customer’s order. It includes fields like product details, quantity, delivery timelines, and payment terms. The sales order plays a fundamental role in inventory planning and customer communication.
3. Why Is Sales Order Required?
Sales order is a central piece of information for the supplier with details on product specifications, quantities required, and other customer-specific details. It makes sure that orders are accurately processed and fulfilled on time.