What is the Accounting Cycle?
The accounting cycle is a systematic process of tracking, analyzing and recording all financial transactions of the company, ensuring accurate accounting records and compliance. It begins with initial data entry of the transaction, followed by complete preparation of financial statements and the closing of accounts. The Accounting Cycle has a series of steps that makes sure about the timely and accurate recording, analysis, and reporting of financial transactions.
Bookkeepers have to keep track of all the accounting transactions recorded from the start to the end of the accounting period. And this accounting cycle records just keeps on repeating every fiscal year as long as the company remains active.
The Accounting Cycle serves as the guideline for maintaining accurate financial and accounting records, helping businesses to produce reliable financial statements. The main goal of the accounting cycle is to prepare financial statements that give the stakeholders relevant financial information, facilitate decision-making and help in assessing the company’s performance and financial position.
The Accounting Cycle of a company encompasses all the accounts, journal entries, debits, credits, general ledger and T accounts, adjusting entries of a full cycle.
You may also read : What is ERP Accounting System?
What is the motive of the Accounting Cycle?
The Accounting Cycle is a boon for the business and the main purpose of it is to monitor, record all the financial activities and future transactions that occur during a specific accounting period. All the financial transactions which are going in or out of the company are recorded accurately.
There are about 8 steps in the accounting cycle explained here. Some steps are more intricate but it is a guide for the accountants or the bookkeepers to vigorously check their financial information before proceeding. More about the steps in the accounting cycle are explained clearly in this blog.
How does the Accounting Cycle work?
Diving deeper into the concept of the accounting cycle, we understand that the accounting cycle is a set of standardised rules that aims accuracy and conformity of the financial statements.
Nowadays, automation of the accounting process and the accounting cycle together have led to the reduction of errors. When considering the manual accounting cycle vs accounting software, automation delivers accuracy and reduces a lot of human effort.
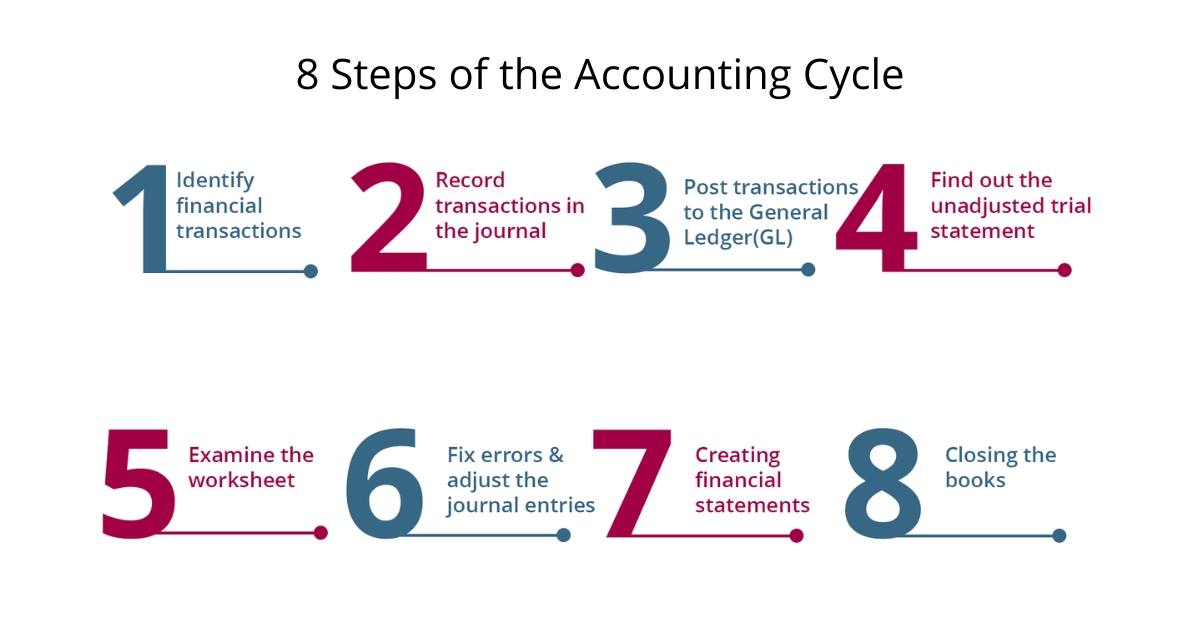
Steps of the Accounting Cycle
The Accounting Cycle comprises 8 steps. The major intent of the accounting cycle focuses on maintaining accuracy in preparing financial statements for a company’s financial transactions.
Step 1: Identify financial transactions
All financial transactions have to be identified and analysed during a specific accounting period. It includes debt payments, expenses, sales revenue, and the cash received from the customers.
In this initial step, it is crucial for the companies to focus on every transaction of the financials. Going through each transaction is a continuous process for the companies to identify transactions, plan the budget cycle, purchase inventory, create customer invoices, make payroll, and collect cash.
Consider that a business is selling custom cushions for Rs 500. The base of this accounting cycle commences.
Step 2: Record transactions in the journal
In the second step, all the details of the financial transactions are recorded in sequential order. Double-entry accounting is applied here. The debit and credit transactions are balanced in the journal entries.
Note that as each transaction is recorded, it is up to the business to decide whether to go for the accrual accounting method(most companies use it) or the cash accounting method.
For example, an invoice is generated for the transaction of a custom cushion in the billing system. Here, the transaction is recorded as a Rs 500 debit in the AR sub-ledger and Rs 500 credit in the revenue sub-ledger.
Step 3: Post transactions to the General ledger(GL)
After the recording approval of the journal entries, they are posted in the General Ledger(GL). What is GL? It provides details and breakdowns of all the accounting and business side transactions in a journal. It is more like a master record or a summary of transactions.
Coming to the example, assume that on one particular day, the custom cushion was sold for Rs 5OO and another two pieces for Rs 400 each. All three sales including the total are recorded in the AR sub-ledger and later posted to the general ledger.
Step 4: Find out the unadjusted trial statement
At the end of the accounting period(quarterly, monthly or yearly), the closing balance of all the accounts is reflected in the trial balance. Here, the unadjusted trial balance is generated. So the trial balance makes sure that the debit balance is in equity with the credit in the financial records. If the debit balances or transactions are unbalanced, it is highlighted.
For example, The debit and total credit balance of the custom cushion are totalled and the unadjusted balance is found out.
Step 5: Examine the worksheet
In this step, all the errors or anomalies are identified from the single spreadsheet. All the lined-up debits and credits from various accounts are examined. If the numbers don’t match, the accountant or the bookkeeper must review the accounts and analyze transactions.
For example, In this step, the debit and the credit of the custom cushion are compared. The accountant finds a discrepancy of Rs 100.
Step 6: Fix errors and adjust the journal entries
In this step, whatever is repeated in the above two steps is continued. Errors are corrected and recorded under the adjusting journal entry. At the same time, even the manual adjustments are recorded such as accruals for expenses occurred which failed to occur in the AP system. It also includes reconciling items that are uncovered during the accounts reconciliation process.
For example, the custom cushion was entered mistakingly as Rs 450. An adjusting entry of Rs 100 is recorded.
Step 7: Creating financial statements
After posting the adjusting journal entries, the company prepares an adjusted trial balance and further a formalised financial statement is created. Most significantly, financial reports are accounting summaries of a company in a particular accounting or reporting period only. Financial statement comprise cash flow statement, balance sheet and income sheet.
For example, After the review and analysis of the accounts of custom cushion, the accountant is content that the financial statements are accurate and are positive for the financial health of the business.
Step 8: Closing the books
Stepping into the final step of the accounting cycle, here the temporary accounts are reset on the income statement. The accounts are closed for a particular year i.e. the revenue and expenses, to zero balances are not carried forward for the next accounting period. The net income or loss incurred is transferred to the retained earnings account. This transaction is considered as a permanent account on the balance sheet and is carried forward for the next accounting period.
For example, this year’s accounting for the custom cushion is cleared and the accountant begins with new expense accounts later.
Importance Of The Accounting Cycle
The accounting cycle enables the reliable tracking and reporting of financial transactions, ensuring the accuracy of financial statements in compliance with regulatory requirements. Here’s why following the accounting cycle is important for every business:
- The accounting cycle helps maintain transparency in business as it systematically analyzes and documents financial records. Further, budgeting becomes simpler.
- Keeps balance sheet and Profit & Loss statements compliant with accounting standards. It enables timely reporting and error-free records.
- Management can take informed decisions through regular monitoring and analysis. Financial data from different accounting periods can be compared to form a strategy.
- Investors can easily monitor the financial health of the company. It improves their business confidence, leading to funding success.
- The accounting cycle is a step-by-step approach to recording and managing financial activities. As a result, it improves the accountability of every transaction.
Conclusion
Finally, we learned that Accounting cycle steps are critical to maintain financials and to analyze the company’s financial position in a particular accounting period. The eight-step accounting cycle is interconnected in identifying and analyzing transactions, followed by documenting them in the journal entry and posting them to the general ledger. The cycle is repeated for many accounting periods as long as the company remains active.
In addition, The accounting of the company is responsible to attract investors, enable informed decision-making and meet compliance with regulatory requirements. ERP system for accounting management incorporates time-saving functionalities such as built-in workflows that automate the accounting process and simplify data entry tasks. Implementing ERP for the accounting process is a boon for the companies to acquire accurate and error-free data.
Accounting Cycle FAQs
1. What Are The 8 Steps Of The Accounting Cycle?
The accounting cycle consists of identifying financial transactions, recording transactions in the journal, posting transactions to the ledger, preparing unadjusted trial balance, examining the worksheet, fixing errors in journal entries, creating financial statements, and closing the books.
2. What Is An Accounting Cycle Process Example?
An example of the accounting cycle process is the quarterly financial close, which involves the recording of all transactions during the quarter, posting them to the ledger, preparing unadjusted trial balance, adjusting entries, creating financial statements and then closing the books.
3. What Is The Purpose Of The Accounting Cycle?
The main purpose of the accounting cycle is to maintain a structured record of every transaction for accurate financial reporting in compliance with accounting regulations.
4. What Is The Difference Between A Journal And A Ledger?
A journal is used to record financial transactions as they happen during an accounting period, while a ledger groups the journal entries based on the individual account they belong to.