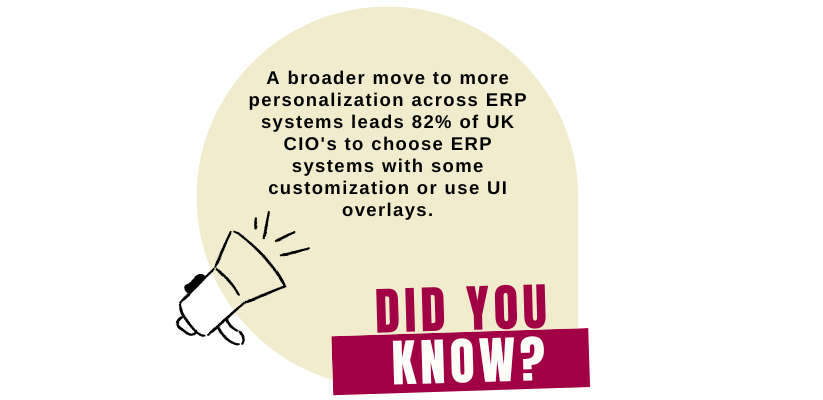
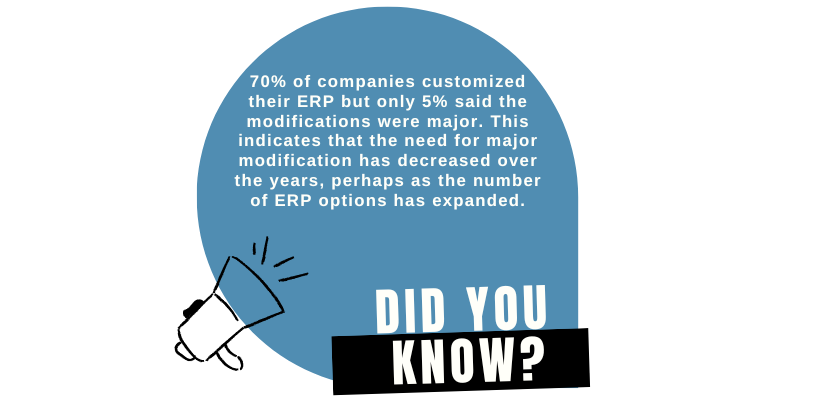
Summary: While businesses of all sizes desire to implement a “vanilla” ERP, it’s not easy as it sounds. It requires immense investment of time, money, departmental collaboration, and employee readiness. Therefore, most companies opt for ERP customization, selecting the most critical modules that allow them to perform business functions. As time passes by, and as business activities become more complex, businesses can integrate new modules. This article will share our experience to help you decide whether you require ERP configuration or ERP customization.

What is ERP customization?
ERP customization refers to adding new modules to your ERP software that you didn’t have before. This change might be because of various reasons:
- Existing modules in your ERP aren’t able to perform new business functions.
- You want to increase the productivity & efficiency of your workforce.
- You want to build better relations with your vendors, suppliers, and distributors.
- You want to establish robust and long-lasting customer relationships.
- You want to save money by outsourcing IT functions to a trusted third-party cloud-service provider.
Time stamps are an excellent example of a new module in your ERP software. They record the exact time when a production job was created and changes made in the orders. This functionality is added to your ERP software without making any changes to the pre-existing modules and hence is a perfect example of ERP customization.
Advantages and disadvantages of ERP customization.
Let’s first check the advantages of ERP customization.
1. You have 360-degree control of your product.
The primary purpose of an ERP system is to increase productivity, enhance efficiency, cut operational costs, perform repetitive work quickly, and allow decision-makers to gain valuable insights from data collected from multiple sources. But one-size-fits-all software might not align with all your business needs. And hence you require a customized ERP system tailored to your specifications and provides absolute control over your business processes & functions.
Off-the-shelf ERP software might lack the exact modules you need to perform business functions, and this is where ERP customization becomes essential. It leverages only the features you need the most, helping you save money on modules you don’t need. In addition, you can brainstorm with all business departments and decision makers to conclude what modules you might need for the success of your enterprise, which increases your control over the ERP system.
2. You will perform better than your competitors
As previously stated, off-the-shelf ERP systems fail to fulfill all your business obligations because they are not built keeping in mind your specific business challenges. Remember that the final goal of implementing ERP software is to help you gain a competitive advantage and only ERP customization can help you get the modules you need to outperform in the market. More importantly, if you fail to implement an ERP system built specifically for your business, you will not be able to understand the market and customer preferences better and, as a result, risk your competitors going ahead of you.
<<<Also Read: 12 Steps To Choosing The Right ERP Software>>>
3. You get a flexible ERP software
Flexibility plays a significant role in the cut-throat competitive world we live in. A flexible solution ensures that new modules can be integrated quickly & efficiently. Moreover, flexible ERP software makes it easy to collaborate with third-party development teams who can quickly understand your business requirements to accommodate new demands. On the other hand, standard software doesn’t provide this level of flexibility and demands more resources and time to offer the same level of benefits as a customized ERP solution.
4. Your ERP system is scalable and can change whenever needed.
Companies flip the rule book quite often. What if you:
- Plan to hire more employees?
- Implement new processes & functions?
- Change company policies?
Therefore, you need customizable enterprise resource planning software that will grow with your business. If you take a customized approach, the software development team will work to scale the ERP solution to your team’s needs by accommodating new services, users, and demands.
5. You will be the real owner of your software
The license of an off-the-shelf ERP software belongs to the software company. Similarly, if you have subscribed to a SaaS model, it means you are paying a subscription fee to the software company. On the contrary, the license belongs to you if your ERP is custom-made. The best part is that you can skip paying a subscription fee to a third-party vendor.
Here are the disadvantages of ERP customization.
1. You can introduce a whole lot of bugs
If you work with a high-quality ERP vendor, you don’t need to worry about bugs and errors during ERP implementation. But if you introduce multiple new features without collaborating with a recognized third-party software development team, you might get into trouble. Remember the general rule: The likelihood of errors is directly proportional to the number of times you customize your product.
2. You might be missing the benefits of Off-the-shelf ERP software
The primary purpose of ERP customization is to add new & improved functionalities to your existing ERP software. But it doesn’t mean you overlook your current software’s built-in features. Moreover, customization sometimes takes a long time, making it difficult to upgrade the system or install regular upgrades. Also, multiple upgrades over a short duration might compromise the basic functionalities of the software.
3. ERP customization might be an expensive affair
The more features you integrate with your ERP software, the more money you need to shell out. Extensive customization will definitely increase your capabilities, but it also comes with a hefty price tag. So, ensure that you implement new modules only when required; otherwise, you will run dry quickly.
4. Beware of over-customization
Sometimes, businesses integrate personalized modules without analyzing whether they are required in the first place. As a result, the ERP software becomes unrecognizable and fails to achieve the objectives it was implemented for. In the worst case, you might have to scrap the ERP software as it no longer serves its purpose.
Defining business objectives before starting to customize your ERP software would be best. This way, you can measure the impact of new modules and whether they are proving advantageous for your business.
Here’s a word of caution: Don’t unnecessarily add new modules to your existing ERP system. You will only lose money.
<<<Also Read: 4 Reasons to avoid Over Customization>>>
ERP Customization vs. ERP Configuration
Customization involves adding new modules to the existing ERP software to increase its capabilities. Changes are made at the source-code level, which requires comprehensive planning. The process involves:
- Establishing business needs.
- Creating a customization plan.
- Offering training to users.
- Fixing bugs and errors.
- Final implementation.
The table below shows the pros and cons of ERP customization.
| Pros | Cons |
| Enables integrating new modules to the existing ERP software. | A highly-skilled team with deep ERP knowledge is required to pull the implementation. |
| ERP vendors mostly provide low-code customization that eliminates almost all cons related to ERP implementation. | Few ERP vendors don’t provide the required support for ERP installation. |
| Unique to enterprise processes and & business workflows. | Some modules require customization in the future. |
| Offers the flexibility to fulfill a business’ operational requirement. | Implementation cost and development time increase with the increase in organizational size. |
| Requires heavy investment of internal resources and robust maintenance. | |
| Sometimes the budget can shoot off, delaying the project. |
On the other hand, ERP configuration allows businesses to add new modules to the existing ERP software without changing the source code. It includes changing the settings of financial reports, time zones, language, currencies, business workflows, and data analytics. In addition, businesses can change the settings based on the requirements of each department (or multiple benefits). For example:
ERP personalization:
- Personalization of field labels, data analytics, business reports, and trends.
- Create the sequence of screen layouts, questions, color schemes, etc.
- Establish departments and employee roles based on the enterprise.
- Use a browser-based interface to publish the configurator to end-users and dealers.
Workflow automation:
- Create discount rules based on item types, customer types, etc.
- Generate BOMs and routings automatically.
- Lay down accessibility and security rules based on the types of customers.
- Define rules to perform automated processes.
- Create discount rules based on item types and customer types.
- Create formulas and rules for creating manufacturing BOMs based on configuration.
What is ERP configuration?
ERP configuration means setting options in the ERP system. But this process is challenging because of two factors —
- There are numerous options.
- Configuration requires technical expertise.
- Existing features should be configured to align with the system’s requirements.
ERP configuration requires appropriate care because most options cannot be reversed once configured. A few examples of ERP configuration are as follows:
- Generating page layouts.
- Setting up language preferences, time zone, and currency.
- Defining role and hierarchy based on access controls.
- Generating a default template and email message for clients.
4 steps for ERP customization
ERP customization is a long and complex process. Here are 4 steps you should implement for ERP configuration.
1. Get a comprehensive understanding of different types of ERP customizations.
ERP customization means extensively modifying the primary code of the ERP software. The process is complicated and labor intensive but error-free. The different types of customizations are as follows:
- Integrations: Third-party vendors design new modules that extend the capabilities of the existing ERP system.
- User Interface: Aesthetic changes based on customer preferences.
- New functions & extensions: Modifying the source code to enhance existing functions or add new modules.
- Forms and documents: Invoices, layout, delivery notes, order confirmation, etc.
2. Abstraction layers come to the rescue.
If customization isn’t managed well, it may negatively impact your ERP for a long time. For example, your system might not be able to install vendor updates automatically. This situation often occurs when your code modifications aren’t aligned with the vendor’s. An excellent solution to this challenge is an abstraction layer that provides an additional interface that protects your customizations from the primary ERP code. Abstraction layers enable businesses to check how compatible a new customization is and also allow making changes to the system without damaging the source code.
3. Evaluate the long-term value of a customization
Start by identifying customizations that have the potential to offer significant value to your organization. It means you should check whether the new customization aligns with your short- and long-term business goals.
Following are a few questions you should ask while assessing the long-term value of customization:
- What value has been added by the customization? And the list of parameters based on which you will calculate this value?
- Can a customization be built in a way such that it doesn’t change the software’s internal architecture?
- Which business challenge is the customization addressing?
- What is the required budget for sustaining the business value?
4. Remove customizations that you don’t require
Business needs and objectives change with time. What appeared necessary when you started your business might not be as essential today. Similarly, if an ERP customization doesn’t provide any value, you should discard it. It’s because every extra line of code unnecessarily burdens your ERP, depleting essential resources.
Here’re three ways of retiring unnecessary customizations:
a. Deactivating or concealing the functionality in the system
If a customization applied to multiple components of an ERP is removed, it will negatively affect the entire system. The best solution to such a problem is to deactivate or conceal the customization so that it doesn’t impact the underlying code.
b. Removing the customization completely
Ask yourself this question: Is the customization negatively impacting a single component or multiple components? A follow-up question might be: If it’s affecting only a single component, then will the rest of the ERP system function appropriately if you remove the customization?
c. Don’t upgrade your system or integrate the customization in the new version.
Use this option only if deactivating or concealing your system functionality will render your ERP useless. The negative side is that your system will not automatically update functions and security updates. The positive side is that your ERP will remain intact, and you can use its basic functionalities at least.