Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) is a software that provides a single unified platform for managing a host of business processes and facilitates a smooth flow of data to optimize the company’s day-to-day business operations.
ERP pulls data from different departments within an organization and builds a Single Source of Truth that provides real-time and accurate access to information, at all levels such as manufacturing, marketing, sales, supply chain, project management, risk management, and financial.
What is ERP Implementation?
ERP Implementation is the process of installing, configuring, and customizing ERP Software and integrating it with different departments across the company such as production, finance, sales, operations, human resources, and so on.
Implementation of ERP across the entire organization or specific department helps you reap the benefits of your new system in terms of reduced costs, increased savings, and enhanced productivity. Typically, it’s recommended to split the implementation process into shorter phases to ensure adherence to the initial plan, mitigate risks, and reduce potential disruptions.
What is ERP Implementation Life Cycle?
ERP Implementation Life Cycle is the structured process of planning, deploying, and customizing an ERP System within an organization to meet specific business requirements within a predefined timeframe. It involves various processes such as defining the project scope, identifying stakeholders, creating a project plan, customizing the system to meet the company’s needs, and providing training & support.
ERP is a broader concept that includes a range of activities such as installing your chosen Enterprise resource planning software, migrating your old data to the new system, configuring & customizing your new system for your unique business needs, and training employees to use it in a logically progressive manner.
The ultimate goal of the ERP implementation life cycle is to facilitate decision-makers with a future-proof system to manage all business units from a centralized location, have a bird-eye view throughout the business operations, and make strong data-backed decisions. With a properly implemented system, the employees and management will no longer find themselves juggling multiple applications for information.
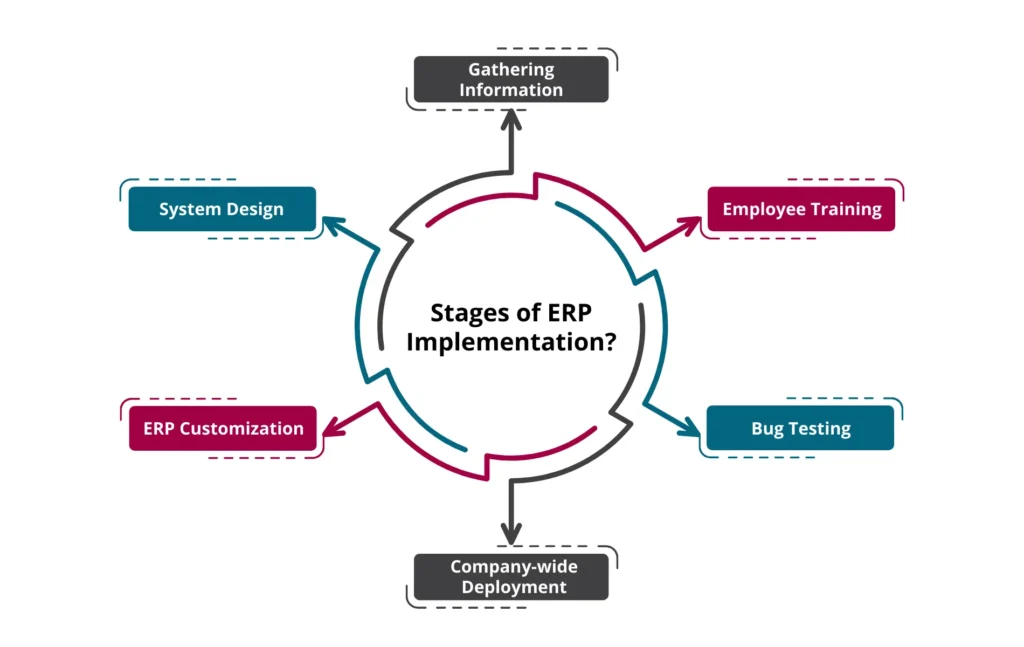
What are the 6 Stages of ERP Implementation?
Now that we’ve discussed what is ERP implementation, let us discuss the stages of ERP implementation :
1. Gathering Information
This is the initial stage in the implementation process. It includes setting up a cross-functional team of employees to pen down specific objectives to achieve and laying out a project plan. The company may also consult with external consultants who have specialized experience, skills, and expertise in implementation.
The goal of this stage is to identify areas of business operations that can benefit from the implementation. It also involves gathering information from all levels across the organization and creating a detailed implementation plan that outlines the timeline, budget, and resource requirements.
The primary duty of the Project Team will be:
- To ensure the implementation process is going according to the plan.
- To ensure end-users have the required knowledge to operate the software independently.
- Make sure that critical business data is stored inside multiple repositories.
- Assisting the employees with any issues they may have with the ERP.
2. System Design
The design stage is the second step of the implementation process. This step involves developing a detailed design of the new system with an intimate understanding of current business processes. The Project Team collaborates with the various stakeholders to define data structures and the look and feel of the new system. They also outline the steps involved in deploying the new system.
During this phase, greater emphasis is placed on gap analysis. It is the process of identifying differences between the current and desired state of the organization. Functional gaps, communication gaps, data gaps, and process gaps, are some of the criteria used.
- The Project Team will gather information from the previous phase and create a detailed plan for the implementation
- The Design phase requires input from all the stakeholders
- The Project Team should create detailed documentation outlining system configurations, and data migration plans
- The Project Team can also use a Project Management Tool to design a thoughtful design plan
3. ERP Customization
There is no one-size-fits-all solution. As each company operates in a unique & complex environment, their needs differ from each other. Thankfully, ERPs are fully customizable. This step involves fine-tuning your ERP to meet the unique needs of your company to gain agility and competitive advantage over your rivals.
There are several benefits of tailoring your ERP for your specific business needs. A well-customized system will ensure the implementation process will align with your ultimate business goals and enhance the functionality of the deployed system.
The process of re-shaping your ERP can be conducted in different ways as outlined below:
- Integrating your ERP with legacy systems, if you already use them
- Custom code modifications and usage of numerous third-party add-ons
- Building Personalized Dashboards for displaying filtered user-specific information
- Creating alerts, triggers, and action events (such as an automated Purchase Management System)
4. Company-wide Deployment
Deployment is the phase at which the ERP goes live- either concurrently across the entire company or partially across certain departments. In this phase, it is important to communicate to all stakeholders about the new system to gather their opinions, feedback, and suggestions.
After deployment, the Project Team closely monitors the new system for any discrepancies and closely interacts with the ERP Vendor for any issues that they might have. For a successful ERP implementation project, it is important that the new system is carefully planned and deployed to get the most out of it.
Here are some tips for effective company-wide deployment of the ERP:
- ERP is a major undertaking. Support of senior management is critical for successful implementation.
- A detailed plan should be in place with a list of tasks to be completed and a budget.
- Employees, customers, and vendors should be communicated with and taken into confidence
- The company can also employ an external consultant to train its employees to use the system.
5. Bug Testing
ERPs are complex and integrate data from different departments. Testing is an essential step in the implementation process to identify potential errors, defects, malfunctions, and performance issues even before they impact business operations. The test results are typically documented and recorded in the system so that the Project Team can communicate with Vendor Support for corrective actions.
The company can deploy various testing methods such as unit testing and system testing. Unit testing is the testing performed on individual modules of the ERP to ensure they are working correctly. In contrast, system testing is performed on the entire system as a whole.
Here are some ways to effectively tackle bugs in the new system:
- When an employee comes across a bug in the system, he/ she should pen down the process to reproduce it again
- The employee should record additional information such as operating system, browser, and ERP version information
- Optionally, the employee should take a screenshot of the bug for better visualization and understanding
- The Project Team should flag the bug depending on its severity. For example Major bug, Minor bug
6. Employee Training
Employee training is a crucial part of the success of the implementation process. This phase involves making employees comfortable with the new changes, explaining the importance of adopting the new system, and providing them with training and support so that they can efficiently use it.
When adequate training is provided to the employees to use the new system, they can become efficient in their work. Ultimately, it can result in a significant productivity boost for the organization. Properly trained employees are less likely to commit errors or mistakes that can cause a significant loss to the organization.
Here are four essential features of successful training programs irrespective of the training methods you implement:
- Collect feedback from trainees and the implementation team to improve the entire training session.
- Start multiple communication channels, including vendor support teams that allow trainees to solve their doubts instantly.
- Create role-based training programs that can be customized based on the user’s learning curve.
- Include tech-savvy people in the training session who help low-level users during the initial days.
Take Your Business Control with Sage X3 ERP
Empower your team and elevate your results with ERP Software
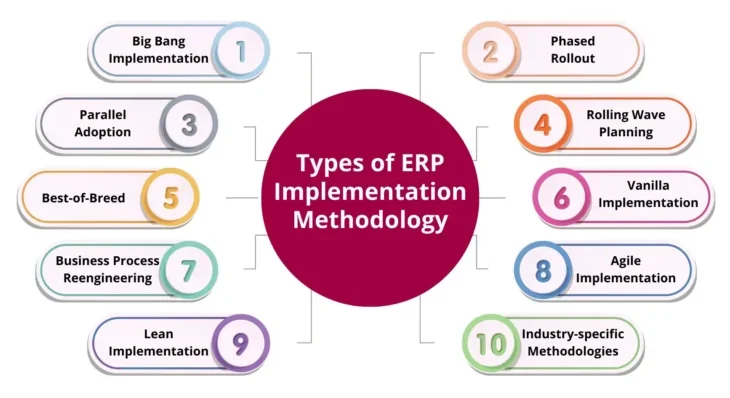
Different Types of ERP Implementation Methodology
After discussing what is ERP implementation, let us move to the types of ERP implementation methodology. There are several ERP implementation methodologies, each of which is tailored to meet the specific needs and requirements of each industry.
1. Big Bang Adoption
The Big Bang Adoption (also called, Bing Bang Implementation, Direct Changeover, or Comprehensive Rollout) involves deploying the entire system in a single rollout. The Big Bang Adoption requires careful planning, analysis, and research to prevent sudden business disruptions, losses, and loss of opportunities & revenues.
2. Phased Rollout
Phased Rollout is a type of implementation methodology of Business Management Software wherein the new system is implemented in phases as a gradual transition, such as one department after another. This type of rollout gives ample time to employees to adapt to the new changes.
3. Parallel Adoption
Parallel Adoption deploys the new ERP in parallel to the existing legacy systems. In other words, the legacy systems continue even after deploying the ERP. This gives safety for the company in the event something goes wrong during the ERP implementation.
4. Rolling Wave Planning
Rolling Wave Planning is a combined methodology that uses an iterative approach, such as implementing certain modules in Big Bang, and other modules in Phased Rollout.
5. Best-of-Breed
Best-of-breed is also known as Selective Adoption. In this implementation methodology of ERP, only useful ERP modules are implemented, rather than the implementation of ERP company-wide..
6. Vanilla Implementation
The Vanilla Implementation methodology is focused on reducing the implementation time and cost. In this methodology, the company relies on the default configurations and settings from the ERP vendor, rather than customizing the ERP for its specific needs.
7. Business Process Reengineering
In this methodology, the existing business processes are redesigned and optimized to align with the new ERP. Typically, this methodology is used in conjunction with other methodologies.
8. Agile Implementation
Agile Implementation methodology involves consistent collaboration between stakeholders. It is a preferred method for those who prefer flexibility and adaptability.
9. Lean Implementation
Lean Implementation involves reducing unnecessary steps in the ERP implementation, lowering wastage, and improving the benefits of ERP.
10. Industry-specific Methodologies
Each company operating in a different industry uses a methodology tailored to its specific needs. For example, a company operating in the production of food products will use a different methodology than one operating in the healthcare sector.
Key Factors to Measure the Success of EPR Implementation
Now that we’ve discussed everything from the ERP’s definition, and what is ERP implementation, to the common pitfalls, let’s move to the key factors used to measure its success.
1. Monetary Savings
A successful deployment should result in cost savings in different aspects of the business operations such as production, inventory management, and sales & marketing. Comparing the pre-implementation costs with post-implementation costs can be an effective way to measure monetary savings.
2. Business Efficiency
The implementation should bring efficiency to various processes in numerous departments. The organization needs to track performance improvements in different areas of operations such as procurement, quality management, and customer support (CRM).
3. Data Accuracy
The organization needs to compare the accuracy of the data pre and post-implementation. It can use various methods such as data profiling, and data validation to assess the quality of the data and track any improvements.
4. User Adoption
Another measure of the success of ERP implementation is the actual user adoption rate. To access the user adoption rate, the organization can track the number of active employees using the new system.
5. Return on Investment (ROI)
Return on Investment (ROI) is a mathematical formula that denotes the profitability of an investment. An increased ROI may indicate the effectiveness of ERP implementation.
Avoiding 5 Most Common Mistakes in ERP Implementation
If you wish to benefit from the smooth implementation process, try avoiding the following mistakes:
1. No Dedicated Team
ERP implementation requires a team of professionals with adequate skills and experience. Not having a dedicated team to look after the complex implementation process can cause failed implementation.
2. Not Anticipating Potential Risks
The implementation is a time-consuming and complex task. It requires the cooperation of different stakeholders for effective implementation. Failing to anticipate the potential risks and challenges can lead to delays, increased implementation costs, downtimes, and loss of business opportunities.
3. Excluding Key Stakeholders
Excluding key stakeholders from different levels of the organization can lead to poor implementation. The key stakeholders include the executive leadership (CEO & CFO), departmental heads who are responsible for the day-to-day activities, and the IT Staff which is responsible for setting up the systems and configuring the IT infrastructure.
4. Lack of Project Roadmap
Project Roadmap is a high-level overview of the project’s goals, and strategic objectives, and a visual representation of what is expected to happen during a course of time. Not defining a clear project timeline can cause chaos. Different employees may work on the same process, leading to a lack of productivity and inefficiencies.
5. Inadequate Employee Training
Your employees must be trained to effectively use the ERP. However, the lack of proper training can lead to poor performance, downtimes, errors, increased costs, and missed opportunities. You may not be able to achieve your intended objectives without training your employees and making them familiar with the new system.
5 Proven ERP Implementation Strategies
Sometimes, the implementation of ERP can take longer than normal and cause disruptions. However, you can simplify the process and avoid pitfalls by following the below ERP implementation strategies:
1. Establish KPIs
Different businesses may have different objectives such as lowering manufacturing costs, reducing inventory stock-out situations, and fixing marketing and distribution issues. In order to gauge the new system’s success, these objectives need to be clearly defined and written down.
2. Data Cleaning
Many companies migrate their entire historical data to the new system which may not be a rational decision. Before migrating your data to the new system, consider whether you really need that decades-old customer order information. Adopting a new ERP system is an opportunity to clean up and rationalize your old data.
3. Communication with All Stakeholders
In order to ensure that everyone is on the same page, there is a need for effective communication with all stakeholders such as management, employees, suppliers, and shareholders. This will promote coordination, standardization, and transparency across all the stakeholders for greater benefits.
4. Leverage a Balanced Approach
Companies need to strive for a balanced approach between customization and standardization to customize the complex system for their use case and leverage the standard functionalities. Ultimately, they will align their system to achieve the goals and long-term success.
5. Continuous Improvements
ERPs need to be regularly updated and maintained to adapt to the changing business requirements and effectively use them to achieve short-term and long-term business objectives. If you don't update your EPR for a long time, you risk running an obsolete and vulnerable system.
Enhance Operational Excellence with Sage X3
In today’s times, there is a growing need for businesses to respond faster to new market changes and have an in-depth look at various business aspects. ERP implementation helps businesses convert long datasets into easily interpretable reports, intuitive charts, and actionable insights. Over time, you will get rid of several disconnected systems, and revolutionize the traditional business practices.
Sage X3 is a ready-fit solution that empowers your business with sophisticated tools and modules to speed up the digitization process and form a collaborative & efficient system of business management. It is an indispensable asset for your business’s growth & success.
Related ERP Articles
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)

What is Implementation of ERP?
ERP implementation is the process of deploying an Enterprise Resource Planning tool in an organization’s internal servers or onto the vendor’s remote cloud servers. To ensure smooth implementation, there is a need for proper planning & research, and collaboration between different stakeholders.
What are the 5 stages of ERP implementation?
The 5 stages of ERP implementation are as follows:
- Initial Research: This is the initial stage that involves evaluating your organization’s goals & objectives, assessing potential impacts of implementation.
- ERP Selection: This stage involves comparing various ERP application tools and selecting the one that aligns with your budget, industry requirements, and functional needs.
- Organization-wide Deployment: This is the actual implementation stage that involves creating a blueprint and deploying the system (either in one shot or in a phased manner).
- Customization: Next, customize your system for your functional needs. You can do so by using various in-house features, as well as using numerous third-party tools.
- Employee Training & Feedback: Train your employees to use your new system efficiently. Gather feedback from your employees to ensure system stability.
What Is The Cost Of ERP Implementation?
The cost of ERP may vary. It depends on different factors such as the size and complexity of your company, the number of modules required, the number of users, training and support costs, and so on. There may be additional costs for consultation with third-party agencies that provide specialized support and services.
Why is ERP implementation a challenging task?
The complexity of the ERP implementation task depends on several factors such as the scope of the implementation (phased roll-out or big-bang), size of your company, and the functional modules you have opted for. In large organizations, the implementation may take longer time (typically, a few months) whereas it may take relatively shorter (typically, a few weeks to a month) in small and medium-sized organizations.
How to Avoid ERP Implementation Delays?
If you wish to avoid ERP implementation delays, you will need to develop a solid and realistic estimate of the timeline during the Planning & Discovery phase. Many ERP projects fall behind schedule because their project planning lacks a strong and realistic timeline.
How Does the ERP Implementation Differ for Cloud ERP & On-premise ERP?
Cloud ERP is installed on the vendor’s server whereas the On-premise ERP is hoisted on the company’s own IT infrastructure. Thus, the implementation steps for both these ERPs vary to a certain degree. Moreover, the On-premise type of ERP requires manual updating whereas the Cloud ERP is maintained and upgraded by the vendor.
What is go live in ERP?
The ERP implementation process goes through different phases. The go-live phase is the final phase when your ERP transitions from the testing environment (sandbox) to the production environment. The go-live method may vary from company to company. Large enterprises with complex operations may adopt phased rollouts to prevent sudden disruptions and ensure continuity in their operations. In contrast, small and medium-scale companies may prefer full deployment.
Schedule Product Tour
"*" indicates required fields