What is Cloud ERP?
Cloud ERP Software is a vendor-hosted enterprise-level & niche-focused solution to drive quick results through powerful data visualization, predictive analytics, and business intelligence

Cloud ERP
What is Cloud ERP?
Cloud ERP is a strategic tool hosted on the servers of your ERP vendor that lets you dig deeper into your company’s performance and manage everything from product design, procurement of raw materials, production schedules, and supply chain to finance.
Many businesses prefer deploying their ERP software on the vendor’s cloud servers as it allows them to eliminate upfront costs and gain remote access to their data regardless of the employee’s physical location.
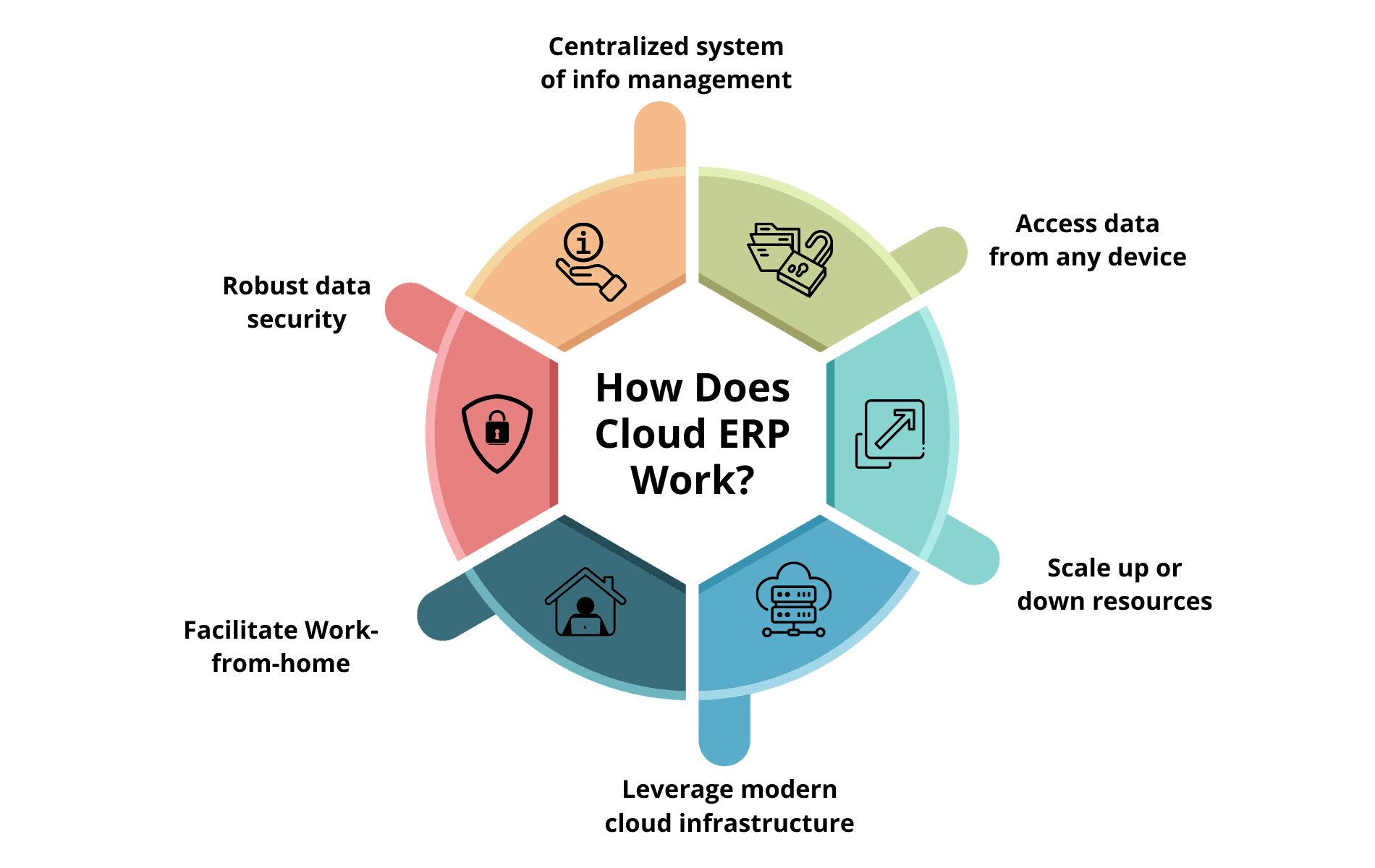
How Does Cloud ERP Work?
Cloud ERP is a modern evolution of the traditional On-premise ERPs. Unlike traditional forms of ERP, it is hosted on the vendor’s servers. The vendor is responsible for managing it and deploying security updates. As such, there is no need to set up a special IT infrastructure to look after the ERP’s deployment, maintenance, and upgradation. Cloud ERP is delivered as “Software-As-A-Service” (SaaS) as the vendor typically charges a monthly or yearly fee. The system has its unique ability to scale up or down resources per the organization’s requirements.
With Cloud ERP, businesses gain a centralized system of information management that integrates data from varied sources (such as production, sales, marketing, and accounting departments) and allows them to access it from any device (such as a computer, tablet, or mobile) without making any upfront investment. Employees can access sales history, consolidated financial statements, and HR tools from their mobile without needing to be physically present in the offices. In the post-COVID era, it has become common for employees to work from the comfort of their homes by simply signing in to their ERP accounts using an Internet connection.
Components of Cloud ERP System
Cloud ERP comes with a comprehensive set of modules. However, a business can choose to include a specific set of modules depending on their strategic business requirements and industry type.
- Business Intelligence Tools that empower businesses to gather, analyze, and share insights to make strongly data-backed decisions
- Procurement Management System that actively tracks the threshold of the stock of raw materials to prevent hindrances during order fulfillment, logistics, and distribution
- Purchase Management System that streamlines procurement of raw materials and packaging materials
- Sales Management System that streamlines order scheduling, invoice generation, shipping, order tracking, and order fulfillment
- Inventory Management System that helps maintain optimum inventory levels and prevent Out-of-Stock and Excess Stock situations
- Supply Chain Management Tools that optimize the supply chain operations and help companies become demand-driven
- Fixed Assets module that keeps a database of all fixed assets to enable asset tracking, registration, and classification
- Lead Management System that helps manage sales pipeline, monitor lead efficiency, and increase the market share.
Features of Cloud ERP Software
1. Remote Accessibility
Cloud ERP enables employees to access organizational data remotely which in turn increases operational efficiency and ensures responsiveness to changing market demands. Your employees can use a mobile app to record new sales without being physically present in the office.
2. Degree of Customization
Each company works in a unique operational environment. ERP allows companies to configure it to meet specific business and industry requirements and gain a competitive advantage. It’s easy to fine-tune it to meet the specific requirements of your company.
3. Data Security Practices
With an increasing number of companies worldwide accessing and storing user’s sensitive data on their servers, it has become incumbent to adhere to data security and compliance regulations. Cloud ERP encrypts users’ data during transit and on the vendor’s servers. It provides multiple internal controls to ensure the company adheres to GDPR, CPRA, and other privacy regulations.
4. Demand Resilience
With the cloud, your business benefits from the “Pay as you go” model. For example, sometimes companies face sudden fluctuations in demand. They can easily scale up or scale down their resources as per changing business needs and ensure continuity in their operations.
5. SaaS Model
One of the problems associated with traditional ERPs is higher upfront costs. Cloud ERPs adopt a Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) model wherein the user pays a fixed amount every month or year, depending on the payment terms. Moreover, the company has the flexibility to choose specific modules and feature sets to purchase.
6. Seamless Updates
As your data isn’t stored on the company-owned IT infrastructure, you don’t have to worry about manually updating your ERP. Your ERP provider releases new updates and security patches from time to time, and the same is automatically reflected in real time.
Take Your Business Control with Sage X3
Empower your team and elevate your results with ERP Software
Top 10 Benefits of Cloud ERP
1. No Upfront Costs
Cloud ERP is hosted on the vendor’s server and accessible using just an Internet connection and a web browser. Thus, there are no significant upfront costs for hardware upgrades and maintenance, deployment, IT staff procurement, server backup, and security.
2. Lower Deployment Time
Cloud ERPs can be deployed more quickly compared to their traditional counterparts. This allows businesses to get up and running more quickly without spending initial time on deployment, setup, and customization.
3. Less Complex
With ERP software, businesses do not need to invest significantly in employing a dedicated IT staff with the required expertise. Furthermore, the ERP vendor provides ongoing support to help with any issues they may have.
4. Remote Accessibility
Data stored on the Cloud ERP is accessible anywhere, anytime, regardless of the device and operating system. Employees, regardless of their departments and subsidiaries, benefit from ongoing access to information no matter where they are.
5. Scalability
ERP software in India is extremely scalable. As your business grows, your ERP will continue to handle the increased workloads, data, and users without compromising system reliability, and performance. Such spikes in demand should neither affect the system’s performance and reliability nor require additional investment in the hardware infrastructure.
6. Ongoing Upgrades
Cloud ERP vendors are responsible for system upgrades. System upgrades are typically carried out during off hours to avoid business disruptions and enable businesses to focus on their daily activities.
7. Robust Security Measures
Cloud ERP vendors implement robust security measures such as data encryption, role-based access controls, and Two-factor Authentication (2-FA), among others, to protect confidential business data during transmission and while it is being stored on the cloud servers.
8. Automated Backups
Backups are one of the most important means to protect business data against hardware failure, malware infection, and accidental overwriting of files. Implementation of ERP using the cloud technology leverages vendor’s servers for storage and data backup purposes. Your company can effectively comply with various data privacy, safety, security, and compliance purposes.
9. Real-time Insights
Businesses can leverage the powerful Business Intelligence tools in the Cloud ERP to identify new market trends, find patterns by analyzing historical data, and get a competitive advantage in today’s highly dynamic business landscape.
10. Improved Operational Availability
Cloud ERP benefits also include the ability to work together on key business projects across different locations, and time zones. As a result, your business benefits from increased operational availability without procuring additional workforce.
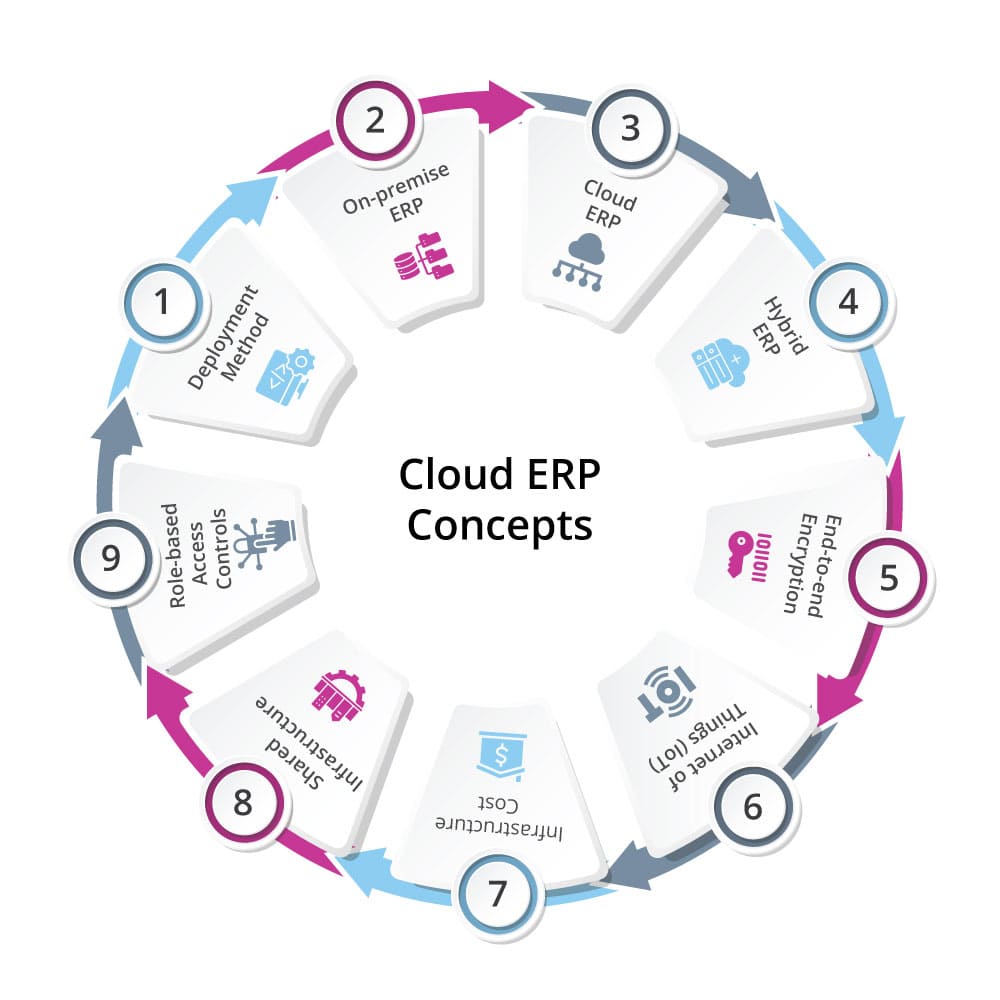
Basic Concepts in Cloud ERP Software
1. Deployment Method
ERP Deployment is the process of installing the ERP on the computer, migrating the data from traditional legacy tools, and customizing the system to meet your unique organizational requirements.
There are multiple ways to deploy ERP Cloud. The exact method of deployment may depend on the requirements of the company, the nature of the industry, and the budget. For example, On-premise, Cloud, and Hybrid ERP. It is up to the company to choose a specific deployment method.
2. On-premise ERP
On-premise ERP is deployed on the company’s IT infrastructure and the company retains complete control over the data. This type of ERP requires a higher upfront cost and the company incurs ongoing expenses for maintenance and upgrade. Furthermore, it needs to set an additional budget for training its IT team and consulting an external consultancy firm.
3. Cloud ERP
Cloud ERP is a modern, cost-effective, and comprehensive solution for most small and mid-sized businesses. Since the vendor is responsible for deploying, maintaining, and securing the system, it lowers the ERP cost and saves businesses from the hassle of deploying a separate IT team. Employees can access the system remotely without needing to be physically present in the company.
4. Hybrid ERP
Hybrid ERP is a combination of both On-premise ERP and Cloud ERP. It offers the “best of both worlds” with a solid base of both On-premise and ERP Cloud infrastructure to meet the needs of rapidly evolving businesses. It is easy to integrate, flexible and offers a cost-effective approach.
5. End-to-end Encryption
End-to-end Encryption is a process of building a secure connection between two parties for confidential data transfer. The use of encryption algorithms allows businesses to store and transfer data with high security standards, and prevent snooping by third parties. Private and Public Keys play a vital role during the entire process. The Advanced Encryption Standard, and RSA algorithm, are some of the popular and reliable algorithms.
6. Internet of Things (IoT)
IoT is a modern technology that enables businesses to connect multiple devices through an online network for inter-communication. ERP offers integration with IoT devices to track machine performance in real time, get timely & accurate data insights, streamline organizational activities, improve productivity, and predict machine downtime.
7. Infrastructure Cost
The deployment of On-premise ERP incurs several costs that relate to the on-premise technology such as the cost of underlying hardware and software. The company needs to plan and allocate a sufficient budget for the servers, storage space, network bandwidth, development software, and operating system.
8. Shared Infrastructure
Shared infrastructure refers to a shared network environment with role-based access to multiple users. The use of shared infrastructure enables businesses to lower their deployment costs and leverage high-quality services.
9. Role-based Access Controls
The Role-based Access Control is a security feature in Business Management Software that allows businesses to determine who can access the system, and who cannot. It allows businesses to prevent unauthorized people from accessing their system and any confidential business data stored on it.
What are Different Types of Cloud ERP?
1. Multi-tenant SaaS
Multi-tenant SaaS is commonly used across many organizations. In this type of Cloud ERP, a single infrastructure serves multiple companies and is hosted on a single server. However, each company’s data stored on the server remains inaccessible to one another. Because the resources are shared among different companies, this type of ERP is comparatively cost-efficient.
2. Single-tenant SaaS
In this type of Cloud ERP, each server is used to store a single ERP infrastructure that hosts data from only one company. As private servers are dedicated to separate ERP instances that host data from a single company, this type of ERP is comparatively expensive.
3. Public Cloud
Public Cloud ERP software refers to the type of Cloud ERP where multiple companies store their data on a single service provider’s servers. Much like the Multi-tenant SaaS, each company’s data is inaccessible to one another. Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure, and Oracle Cloud are some of the popular examples of Public Cloud.
4. Private Cloud
Private Cloud based ERP software refers to the use of a computing environment dedicated to only a single company, and no other companies. A single company is in complete control of the server infrastructure and any data stored on it. Due to the nature of the server infrastructure, Private Cloud is highly flexible and customizable.
5. Hybrid ERP
As the name suggests, a Hybrid ERP application is a combination of both On-premise and Cloud ERPs. It is gaining momentum due to the various advantages that it offers. For example, the cost of setting up a Hybrid ERP is much lower compared to an On-premise ERP, and it is less complex in nature.
Cloud ERP Vs On-premise ERP
| Cloud ERP | On-premise ERP | |
| Cost | Lower upfront cost The company pays a monthly/ annual subscription periodically. | Higher upfront cost. The company pays upfront licence fees and invests in hardware infrastructure. |
| Customizationsc | Offers fewer customization options. | Offers broader customization options. |
| Scalability | As your company grows in size, you can acquire additional server resources to meet your operational needs. | Offers limited scalability. The user is largely constrained to the limited hardware capacity of the deployed machines. |
| Updates | Updates are released and maintained by the vendor. | The user is solely responsible for deploying updates. |
| Deployment Time | Deploying a Cloud ERP can be faster and easier. | On-premise deployment may take longer time due to additional customizations. |
| Performance | The system performance largely depends on the vendor’s server capabilities. | The system performance largely depends on the quality of the hardware owned by the user. |
| Data Compliance | Easier compliance with the industry data standards. | Complying with the industry data standards may require special provisions. |
| Data Security | The vendor is responsible for data security. | The user is responsible for data security. |
Limitations of Cloud ERP
While Cloud ERP is a useful tool, it is not free from limitations:
1. Internet Connectivity Issues
The concept of Cloud based ERP revolves around the use of the Internet to store and transmit information. You will need a stable and high-speed Internet connection to ensure fewer disruptions.
2. Limited Customizability
While On-premise solutions offer a higher degree of customizability, their cloud counterparts typically offer limited customizability and fewer templates to work on.
3. Long-term Cost
Cloud comes with the short-term convenience of periodic payments. However, it may prove costlier in the long term.
4. Server Downtimes
Server downtimes are common with the low-quality & unreliable ERPs. Frequent service outages can have a negative impact on your business’s reputation and lead to monetary losses.
Criteria for Selecting the Right Cloud ERP
Server downtimes are common with the low-quality & unreliable ERPs. Frequent service outages can have a negative impact on your business’s reputation and lead to monetary losses.
Here are some important factors to consider during the Cloud ERP selection process:
1. Fulfils Industry Requirements
Each business has unique requirements. Make sure that your vendor deeply understands your organizational and industry requirements, and provides the required capabilities to meet them.
2. Scalable with Demand
Scalability is a vital factor when it comes to ERP in general. If your ERP isn’t scalable, you may run out of different issues as your business increases in size and operations. Go with an ERP that can handle an increasing load of demand without performance issues.
3. Organization-wide Integration
Are you one of those businesses that prefer to keep using multiple legacy systems? If so, you might want to make sure that your new ERP is compatible with the existing legacy systems. Otherwise, you risk running into data integrity and various other technical difficulties.
4. Cost-efficiency
Budget is a crucial deciding factor when it comes to ERPs. The cost of an ERP may vary from product to product. An ERP’s cost may include licensing fees (or monthly/ annual subscription charges), updates & maintenance charges, implementation charges, third-party consultation costs, etc.
5. Vendor Track Record
Remember, ERP is a long-term investment. Make sure that your vendor has a positive track record of regularly releasing new feature updates, performance updates, and bug fixes. This will ensure continuity in the business operations and security of your confidential information.
6. Data Security
Does your ERP have strong data protection safeguards in place to protect your company’s confidential information? In today’s world where businesses have to adhere to stringent data protection regulations, such data security features are highly essential.
Unleash Your Business Performance with Sage X3
In today’s era, business processes have become increasingly interrelated and complex. Cloud ERP provides a robust framework to access data in real-time across different departments without worrying about data silos, obsolence, and inaccuracy.
Sage X3 is an all-encompassing solution incorporating modern technology, extensive customization, and deep analytical features. It offers a robust array of features, multi-layer data protection, and richly detailed reports to act intelligently in rapidly evolving business circumstances.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is Cloud ERP System?
A Cloud ERP System is an integrated Enterprise Resource Planning tool that comes with a Subscription-as-a-Service (SaaS) pricing model and no upfront costs. It saves business owners from the hassle of regular maintenance & upgradation, allowing them to focus on what truly matters — their everyday business operations.
Why is Cloud ERP Better?
Cloud ERP has become a new normal, especially in the post-pandemic era. It is a better choice compared to traditional On-premise ERP particularly because it is cheaper, and offers remote accessibility and superior performance. It offers robust security features, automated backups, and data recovery to deal with data disasters and protect confidential business data against online theft and cybercriminals.
Why Are Modern Manufacturing Companies moving to Cloud ERP?
Here’s why modern manufacturing companies are moving to the cloud ERP:
- Manage data anytime, anywhere with a mobile-first solution
- Lower initial costs (annual/ monthly subscription fees)
- Enhanced flexibility, scalability & accessibility
- Stringent industry-standard data security
- Integrate seamlessly across departments for streamlined workflows
- The vendor is responsible for maintenance & upgradation
Is Sage X3 a Cloud-based ERP?
Yes, Sage X3 is a fully cloud-based ERP that offers robust integration with your legacy applications, extensive customization options, and seamless data management across multiple devices. It transforms your traditional business processes and offers multi-country, multi-currency, and multi-legislative capabilities.
What is the difference between Cloud ERP and SaaS ERP?
Cloud ERP and SaaS ERP are not different concepts. Cloud ERP adopts a Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) pricing model that allows businesses to pay a regular recurring subscription fee, eliminating the upfront costs associated with traditional ERPs. This enables small and medium-sized enterprises with a limited capital base to capture new opportunities and streamline their business activities.
What is the difference between Cloud ERP vs On-premise ERP?
Cloud ERP is a modern SaaS-based solution that offers intelligent tools, advanced algorithms, and world-class data security with a centralized vendor-hosted data management. In contrast, On-premise ERP hosts your data internally on the organization’s in-house servers. It is a traditional solution that requires a significant upfront investment, and an expert team of engineers responsible for server management and ERP maintenance & upgradation.
Schedule Product Tour
"*" indicates required fields