What is ERP ?
Enterprise resource planning (ERP) is a software that helps you streamline daily business operations, including project management, procurement, accounting, supply chain management, risk compliance and management, human resource management, and more.
What is Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) ?
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) is a business planning and management software that provides a sweeping overview of your business activities and automates core business activities such as procurement, production planning, inventory management, sales, customer support and supply chain. ERP is considered a backbone of modern-day businesses. As they operate in a highly complex and competitive environment, they need an agile system that takes care of their everyday business needs and promotes strategic decision-making.
Enterprise Resource Planning comes with a wide range of features and capabilities. It eliminates manual work and makes business processes less error-prone. It provides the capability to get real-time information about various ongoing processes for expense tracking, project planning, seamless integration, and other purposes. It helps decision-makers make strategic decisions based on a single source of truth, optimize resources, reduce costs, and increase profits.
ERP system helps streamline numerous business processes such as manufacturing, supply chain, raw material procurement, human resources, finances, and others. By integrating these processes under a single platform, an ERP software avoids data duplication and maintains the integrity of the information.
Why is ERP Important?
ERP solution offers integration, intelligence, and automation required to carry out routine business operations. It is the central nervous system of a business. All the organisation’s data is saved in the ERP solution to offer a single source of information across all departments.
ERP software solutions are an integral part of businesses since they accurately plan and coordinate the numerous business functions. One major benefit of ERP solutions for companies is tracking the available inventory and delivering customer orders. Additionally, it can compare supplier POs and predict demand in the future, thereby guiding companies to make informed decisions.
ERP solution helps the finance department to close the books instantly while the sales team leverages it to streamline all customer orders. Shareholders & the banking sector require ERP for precise financial records that can be developed through the system’s reliable data and analytics.
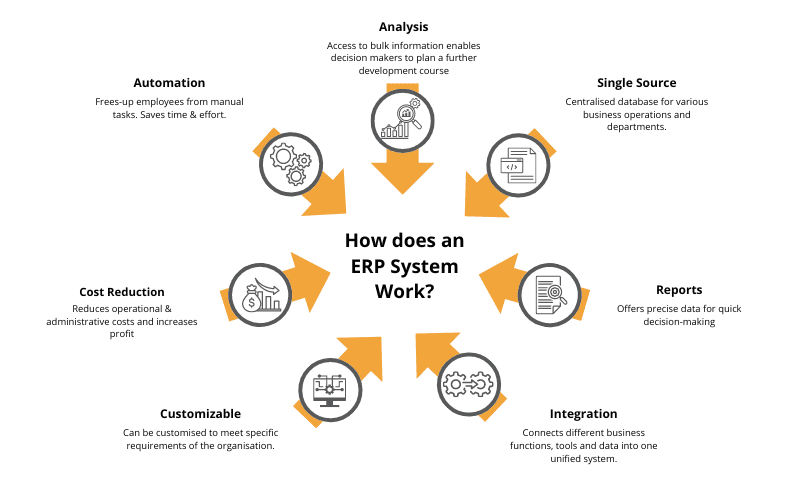
What is ERP and how does it work?
An ERP System consists of multiple modules, with each module focusing on an individual business process. A business has several business areas, such as accounting, human resources, production, research & development, sales & marketing, supply chain & logistics, and more. The ERP integrates these different modules under a single platform with a centralized database, enabling seamless streamlining of these processes.
The companies can select the modules they wish to use while implementing an ERP solution for their business. With an ERP solution, companies get an integrated system with a shared database, real-time data and dashboard, unified user interface, and in-depth insights. Hence, companies can synchronize their activities to achieve efficient performance metrics.
The ERP system supports industry-specific needs, be it the system’s basic functionality or app extensions that can be easily integrated with it. An ERP solution can be purchased as an on-premise (licensing model) or as a SaaS (cloud subscription model).
With the ERP system, real-time data can be easily turned into business functions and workflows across all departments. It can deliver outstanding results and ensure on-time delivery and accurate data entry. The ERP vendor can tweak their system to seamlessly integrate their other commonly used solutions, for a cohesive experience.
Who uses ERP?
ERP Software is used worldwide by businesses of all sizes across different industries. Businesses that are suffering from supply chain visibility issues, inventory mismanagement, a lack of strategic foresight, and increasing production costs are turning towards ERP.
ERP empowers these companies with modern technology to automate their operations, reduce human errors, and gain a sweeping overview of their business operations. It empowers them with real-time actionable insights, strategic decision-making, and operational efficiency to compete & thrive in today’s highly dynamic business environment.
Top Industries Leveraging ERP Software
Food & Beverage
Alcohol
Pharmaceuticals
Advertising
IT Services
Furniture
Manufacturing
Auto Ancillary
Pharma Trading
Packaging
Medical Device
Chemical
Plastic
Brewery
Logistics
Automotive
Upgrade Your Business DNA with Sage ERP
Empower your team and elevate your results with ERP Software
How ERP Empowers Different Business Functions
In every industry, ERP manages several job functions, including –
➤ Supply Chain Management
Employees that are engaged in operations, especially those including inventory planners, warehouse managers, purchasing agents, senior supply chain leaders, etc., depend on ERP for a seamless and continuous flow of products from supplier to customer. They can fetch accurate and detailed information through the system and easily prioritise orders, discard supply chain disturbances, increase timely shipments, check manual processes and more using supply chain management software.
➤ Sales & Marketing
ERP solution is responsible for increasing productivity while gearing for better outputs for the sales team through lead management system. Better results are also expected through the execution of tracking interactions of the company. With the sales management system, sales representatives can easily pen down the discussions and can change the current or past status of the prospects as per the movements in the sales funnel. Once these details are ready, the marketing personnel can manage their insights through every channel. Additionally, they can calculate the efficiency of those messages and channels to allocate adequate budgets.
➤ HR Management
The main use of ERP for the HR department is to track the data of all employees and focus more on workforce trends using the ERP solution. The system can quickly get the contact information and other details for every employee. An HR can also look after various department-wise metrics like average pay by title, retention, and promotion rate to engage their staff in a better way.
➤ Accounting & Finance
Best ERP software in India helps the accounting & finance team track and report every single transaction and other financial data in the system. It also includes payroll, Accounts Receivables (AR), and Accounts Payable (AP). The system helps Financial Planning & Analysis (FP&A) experts convert detailed financial data into predictions as well as report on cash flows, expenses, and revenue.
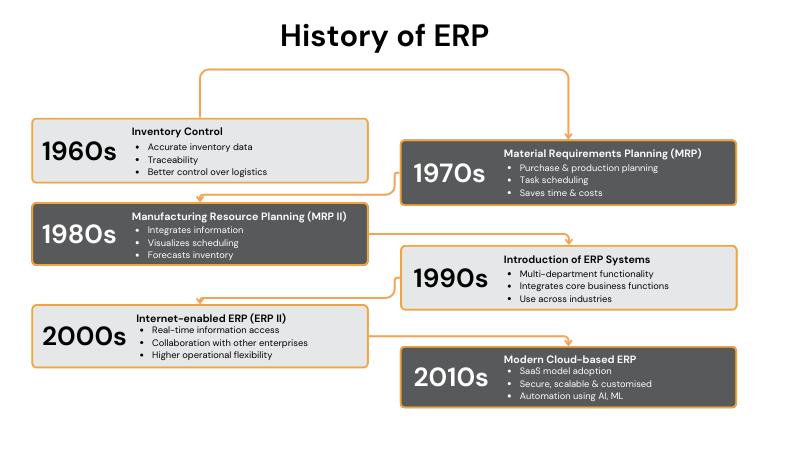
History of ERP
The history of ERP dates back 100 years with the development of the Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) model, computed for manufacturers to minimize total inventory costs. During the period of 1964-1990, EOQ evolved into Material Requirements Planning (MRP I) and Manufacturing Resource Planning (MRP II), which provided superior capabilities. In the 1990s, a full-fledged ERP was developed to integrate multiple business functions.
1910s: Ford Whitman Harris develops the Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) model to calculate optimal order quantity while keeping inventory costs low.
1960s: Introduction of Mainframe computers for finances-related tasks such as ledger maintenance, reporting, etc. In 1964, Black and Decker develops Material Requirements Planning (MRP) solution which integrated EOQ with computers.
1970s: MRP I streamlined material planning in manufacturing, utilizing computer processing, databases and algorithms for Bill-of-Material (BOM).
1980s: Development of MRP II with integrated modules across accounting, inventory management, etc. which had a central database.
1990s: Gartner invents the term ‘ERP’, which were client-server systems that could automate basic processes like accounting, payroll, inventory management and order tracking.
2000s: Introduction of cloud-based ERP with web applications, improved KPIs and analytics, field services, dashboards, mobile app support & more.
2010s: ERP in the form of SaaS and XaaS applications providing enhanced remote web-based solutions which integrated modern technologies like AI, machine learning, IoT, and secure databases, to provide comprehensive ERP Solutions.
The Future of ERP System
The market has continuously fluctuated in recent years, giving a rising call for digital transformation and ‘ERP’ stays at its core. As per the recent survey made by Forbes, ERP is ready to transform the business verticals and also to customize the customer needs, business objectives, and more.
With evolving digital technologies, businesses are quickly changing the way they operate. Below are the major trends that will be geared in the coming time-
➤ ‘Cloud’ will be top preference
The significance of cloud ERP will be intensified in the future since several companies are looking for ‘anytime’ and ‘anywhere’ access along with minimised cost of technical and hardware support. As per recent reports, more than 60% of companies are choosing cloud software rather than on-premises software.
➤ Industry-specific system
One of the biggest future trends in ERP will be user industry-specific systems. Several suppliers, customers, and employees seek personalised operations to meet their business requirements. The changing workforce and statistics bring no-code and low-code platforms concepts, especially in the manufacturing industry.
These tools help users to get the best customer experience as they wish, instead of learning the new software, which consumes precious time. Also, with the ERP, customers can enjoy personalised dashboards to boost customised chat and workflows, AI-based search, and more.
➤ Two-tier ERP
With two-tier ERP software in India, all small and medium-sized companies can utilize two solutions simultaneously. The concept is best suited for those companies having multiple locations and subsidiaries. The two-tier methodology is on a high edge since it is tied to cloud computing, making ERP systems completely accessible for all organisations.
➤ IoT (Internet of Things)
The Internet of Things establishes connectivity among multiple devices and computer systems. It offers enhanced asset management, forecasting, efficiency, communication, business intelligence and more. The changing consumer behaviour has led to the deployment of IoT in businesses. Hence, it can be observed in varied industries and has become an integral asset for them. This technology is at its peak nowadays, and there is no sign of its downtrend.
➤ Mobile ERP
In the modern tech world, everyone is on their smartphones, tablets, etc., which is why mobile ERP is becoming the most powerful solution in the industry. The mobile ERP can automate processes like marketing, accounting, and business. It also simplifies the interactions to make a few scenarios accessible to the user.Mobile ERPs are designed with a user-friendly interface that can assist users in undertaking their daily business tasks. Employees can complete tasks including time tracking, call logging, cost reporting, and more. Additionally, they can check and view the vital workflow status right from their mobile phones.
Core Modules of ERP
An ERP tool involves several modules having varied features customised for different business aspects. These modules go beyond finance and other major functions like customer interaction and supply chain management.
Let’s have a quick look at the widely used ERP Modules:
1 – Supply Chain Management
The supply chain management software helps businesses monitor the supply and goods movements throughout the supply chain. It also undertakes various other business operations like transportation, logistics, warehousing functions, real-time inventory management, etc. It makes the supply chain a completely transparent process and increases flexibility.
2 – Finance & Accounting
The finance and accounting module is one of the essential ERP modules which helps companies to understand their financial status and build their future vision. The key functions of ERP accounting software include managing the General Ledger (GL), Accounts Receivables (AR), and Accounts Payable (AP). It creates and stores major financial documents, such as payment receipts, tax statements, balance sheets, and more.
AR Automation can quickly automate operations related to cash management, vendor payments, etc., aiding the accounting team to close their books on time and match with the present revenue recognition levels.
3 – Enterprise Asset Management
EAM module (enterprise asset management) helps asset-related businesses reduce downtime by maintaining their equipment and machinery to run at the highest productivity levels. This asset management software revolves around predictive maintenance, asset operations, health & safety, environment, scheduling, and more.
Asset management software offers the ability to monitor purchase and placement of assets, preventive maintenance functions, asset devaluation, and monitor assets. Some additional capacities of the module include offering complete support for inventory and warehouse management business functions.
4 – Project Management
The project management module of ERP helps industries in managing projects along with their details. It involves managing and organising the raw material, tracking project status, accounting for needs, etc. All details with respect to the project are saved in the records of this module.
5 – Production & Manufacturing
While the manufacturing process is going on, the ERP software for manufacturing can easily upgrade the current status of all the goods that are in process while assisting organisations in monitoring the current output as compared to the predicted output.
This is among the major ERP components that can also offer an instant image of the shop floor while fetching data on items in progress and also of the finished products. It can also analyse the time required to generate an item and compare its supply with the predicted demand. This helps plan the production as per the market requirements.
6 – Quality Management
The quality management module of ERP system checks and maintains the quality of the manufactured goods as per the certification standards. It also helps to analyse various checkpoints to monitor the quality while preventing defects in manufactured products.
7 – Customer Relationship Management
The CRM software, one of the key ERP components, saves all customer and prospect information in the database. The data also includes all communication history with the customers along with the time, date, and emails. The CRM software can enhance customer service since the employees can easily access all data as and when needed.
8 – Inventory and procurement
The procurement software helps manage the purchase of finished goods or raw materials. It can automate PO (purchase orders) and quote requests. When it is linked with a demand planning feature, it can also reduce under-buying and over-buying situations.
The inventory management software can display various inventory levels below the SKU levels by updating the numbers in real-time. It also measures important metrics related to the inventory. It helps to optimise stock based on future and present demands.
9 – Service
The service module of an ERP system helps organisations deliver a customised and trustworthy service as per the customer expectations. It involves various tools for field service management, service-based revenue streams, spare parts, in-house repairs, etc.
10 – Human Resources Management
HRM (human resource management) module includes features of workforce management application and delivers some add-on capabilities. HRM acts just like a customer relationship management module for employees. It has precise records of every employee and can also store important documents like job descriptions, performance reviews, and more. It can effortlessly track leaves, hours worked, and paid time off, etc.
11 – R&D and Engineering
With this module, you can easily integrate with all departments that sell, service, and manufacture products with reduced cost and provide the highest quality. It offers the ability to monitor purchase and placement of assets, preventive maintenance functions, asset devaluation, and monitor assets. Some additional capacities of the module include offering complete support for inventory and warehouse management business functions.
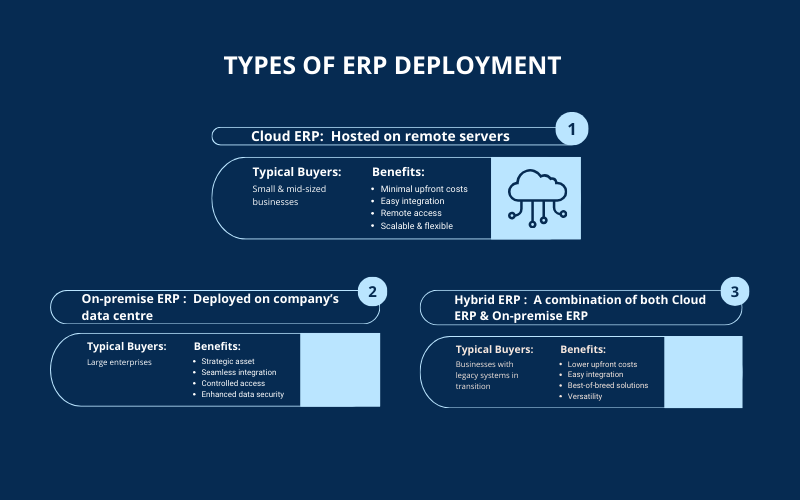
Types of ERP Deployment
ERP systems can be implemented in a number of ways, such as in private cloud, public cloud, and on-premise, or even in various hybrid scenarios having different environments. These types of ERP software can be deployed as per the business requirements.
Let us see the notable benefits of each type of ERP deployment which would suit your business the most.
1 – Cloud ERP
The cloud ERP software is hosted in the cloud while it is delivered over the internet as a service. The cloud-based ERP solution provider looks after the regular maintenance, security, and updates. Today, cloud ERP is the best deployment method owing to its huge benefits like minimal upfront costs, easy integration, high agility and productivity, etc.
2- On-premise ERP
On premise software helps you control everything and is considered as the traditional model to deploy the software. The ERP system is installed in the data centre at your preferred location. The maintenance and installation of the software is the responsibility of the team. Today, a number of companies that have been deploying on-premise ERP systems are upgrading to cloud ERPs due to their agile nature.
3- Hybrid-ERP
Hybrid ERP is especially relevant for those companies who are looking for the benefits of on-premise and cloud ERP deployment to meet their business needs. Here, some applications and data will be saved in the cloud and the rest will be saved on-premise as per the company’s requirements. Usually, hybrid-ERP is referred to as a two-tier ERP system.
4- Open-source ERP
Open source ERP is a very cost-effective and free option suitable for some organisations. A lot of open-source ERP providers help companies to implement their software free of cost. Also, they may charge a very minimal annual fee in case the user needs cloud access.
Features of ERP
An advanced ERP can have a number of functionalities as per the modules they have and the industry standards they cater to. Below are the most important features that all ERP systems should have–
➤ Centralized Database
The system should have a common database with having centralised information offering a 360-degree view of the organisation. Also, it should have consistent and shared data. This single source of real-time information eliminates the need to manually merge various databases.
➤ Data visualisation
It is one of the vital features of ERP that showcases the visual presentation of important information through KPIs, dashboards, etc and also helps in making informed decisions.
➤ Automation
This key feature of ERP software has the ability to automate redundant tasks including invoicing, reporting, processing, payroll, and more. It reduces manual duplicacy and manual data entry, reducing errors, and saving a lot of time. With automation, your staff can focus on the important tasks that take advantage of their skills and knowledge.
➤ Stable Interface
Throughout all roles and departments, every team member uses the same user interface and has the same user experience with the ERP system. For example, modules for inventory management, finance, and HR look the same and have the same shared functionality. A stable UX/UI can give you efficiency profits.
➤ Data analysis
ERP surpasses all data silos. Whenever you try to mix and match data from any specific part of your business in insightful reports, you are keeping focus on the outperformed areas along with those failing to fulfil expectations. The team executives can then check the issues and resolve them instantly.
➤ Deployment choice
This must-have feature is one in which users should choose the type of system they want to deploy at their workplace. They can choose from Cloud, hybrid, and on-premise systems.
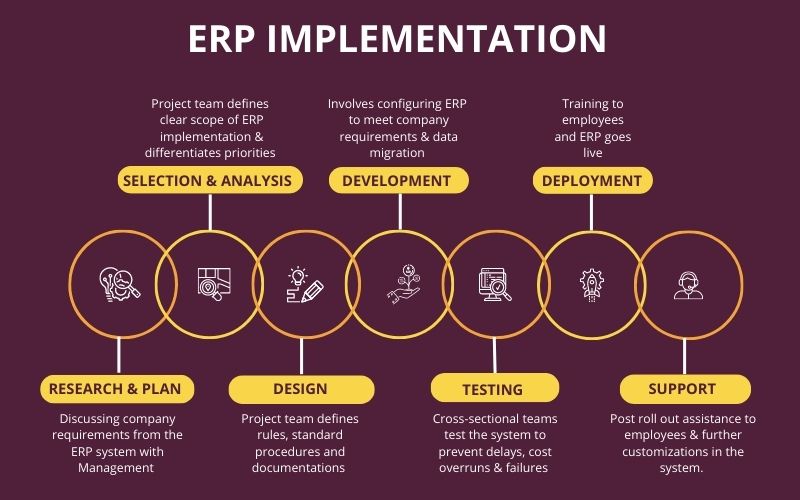
Steps of ERP Implementation
Without proper preparation, ERP implementation strategy may consume a considerable amount of time and money. The time and money required by the implementation of ERP depends on a number of factors, including system complexity, implementation strategy, company size, and specific resources kept aside for it.
→Steps of ERP Implementation
Preparing well for the ERP implementation process will pay off for sure, and companies can also avoid key challenges by preparing a detailed plan for the ERP implementation.
Below are the major stages of the ERP implementation process-
1 – Research & Plan
One should get the cross functional team on the same page and then, discuss and analyse what are the company requirements from the ERP software. The prime function of this team would be to chalk out poor processes along with the obstacles to business growth.
2 – Selection & Analysis
Once the team has all the required documents, it should analyse the offerings and choose the suitable platform that can solve the existing issues in the system. It should meet every need of the department while augmenting the company’s growth.
3 – Design
In the designing phase, the ERP implementation team checks if the system can withstand the existing configurations and workflows and also checks which processes should be amended. This is the perfect phase to check for any customizations requirements.
4 – Development
During the development phase, expert technical professionals configure the software to achieve the desired goals. They also start migrating the organisations’ data to the new system. This phase also lets you decide how the employees will be trained and start scheduling sessions to get the required outputs.
5 – Testing
This is a step which should not be skipped for any reason. The testing phase makes sure that everything needed is working as expected so that you can repair any problems before they occur in the future. It is highly advised that all cross-sectional teams should be present while testing the system.
6 – Deployment
The deployment phase is the ‘go-live’ phase. Companies should train their employees and guide them to accept the change in the system functions. Some companies choose to roll out all modules at a time while some choose to release a few modules at the beginning.
7 – Support
The support stage is the ERP implementation strategy, which ensures that the users can take advantage of the ERP system and may also include some additional configurations.
Cost of ERP
The cost of ERP depends on the vendor, deployment model, and modules. Usually, the total cost of ERP software may range from $10,000 to a million dollars each year.
Cloud-based ERP, especially SaaS options, has reduced upfront costs as compared to on-premises software. As mentioned earlier, the ERP cost is also based on the modules your business requires. The final solution may have basic functionality for basic order or inventory management functionality. And if modules are customised, they will incur some additional fee.
In the case of on-premise ERP solutions, organisations can buy a permanent licence, which is costlier when compared to cloud-based options.
How to Choose the Right ERP Software for your business?
There are a number of factors that should be considered while selecting an ERP solution. These factors include company size, deployment model, and required capacities. One should always look for vendors who have proven records of successfully working with companies in your industry.
Additionally, one should consider the ERP software provider’s roadmap for latest technologies like blockchain, IoT, Artificial Intelligence, and more.
You should start with those modules that are important to your business. For example, companies can start with the finance module to automate main accounting operations. Similarly, companies with a larger number of employees should consider HRM (Human Resource Management) systems for improved employee experience and enhanced company reputation.
Finally, choose an ERP package for your company that is scalable enough to enhance the features and modules to help you grow your business.
While choosing an ERP solution, follow these steps to save time and money as well as avoid errors:
Conduct a process review and analyze the ERP software requirements
Align the requirements of an ERP system with the company processes
Evaluate the total cost of ERP solution ownership and maintenance
Develop a realistic ERP Implementation Plan
Track the Return On Investment (ROI) by the ERP Solution
Research prospective ERP software vendors thoroughly
ERP Integration
Currently, ERP software offers a broad range of business functionalities while still it needs to sync with other applications like CRM, HCM software, industry-specific solutions, e-commerce platforms, as well as other ERP systems. With proper ERP integration, businesses can gain a clear view of data from various systems and enhance business process effectiveness. It can improve customer experiences while facilitating connection across all departments as well as business partners.
The advanced ERP systems are quite agile in nature and can be easily integrated with a broad array of software product APIs (Application Programming Interface). Some other methods for ERP integration involve iPaaS (integration platform as a service) and ESB (enterprise service bus).
iPaaS technology can quickly sync cloud ERP software/ on-premise ERP software from third parties or from the same vendor. These platforms require very low coding or even no-coding and are very inexpensive and flexible.The major advantages of iPaas include support for a wide array of use cases, such as IoT integration, automatic API generation, prebuilt content, and more.
One vital piece of information that needs to be considered when it comes to ERP integration is that the more data that is fed into the ERP system, the more value the system will provide.
Limitations of ERP
Though ERP offers value to companies in all ways, companies may also face some challenges while implementing it or even developing a building case for the system. So, it is crucial to understand the blockages prior to adopting an ERP system. However, it is to be considered that these blockages can be removed by having a detailed plan and by choosing an appropriate ERP vendor.
Things to keep in mind before you get ready for ERP implementation-
- Higher Upfront Costs : Traditionally, ERPs were expensive due to higher upfront costs. Thanks to modern cloud ERP, things have changed.
- Need for Training : Much like any other modern technology, ERP requires a deep learning curve.
- Usage Complexities : Some low-quality ERPs may come with a complex interface. You can avoid it by scheduling a demo before making your purchase.
- System Maintenance : In the early days, businesses were responsible for maintaining their ERPs. With cloud, the vendor is responsible for maintenance & upgradation.
- Inefficient Support : Some low-quality ERP vendors may not provide efficient support, leading to delays and confusion.
- Implementation Delays : The implementation process can get delayed due to data conversion issues and other technicalities.
Related ERP Articles
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is ERP in simple words?
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) is a strategic tool that empowers businesses with business-critical functions required to reduce labor-intensive operations, fix operational bottlenecks, and improve agility in decision-making.
What is an ERP example?
Sage X3 is a popular example of ERP used by small, medium, and large enterprises across different industries. It offers a high degree of system flexibility & customizability, along with extensive planning, forecasting, and data analytics.
What are the 5 components of ERP?
The 5 components of ERP include inventory management, supply chain management, customer relationship management, human resource management, and financial management. These pre-built components in a ready-fit ERP allow businesses to streamline different business functions and tackle industry-specific challenges.
What is the need of ERP?
An ERP is a modern-day business planning solution that supports critical business activities. Here’s why your business may need it:
- Streamline your business activity
- Gain visibility across different functions
- Improve operational efficiency and foster growth
- Gain market insights and Business Intelligence
- Generate project-wise report and find cost-saving opportunities
- Track and allocate your resources efficiently
- Expedite billing operations and enhance accuracy
What is an Extended ERP?
An Extended ERP is considered a more comprehensive version of a standard ERP that handles all external business operations. It provides a more comprehensive view of your business functionalities beyond the basics. It primarily deals with sales-force automation, e-commerce integration, shipment tracking, and external data integration.
Which is not a function of ERP?
While an ERP is a robust system and a good match for your company, it’s not a one-size-fits-all solution. It doesn’t include anything and everything. It doesn’t help with every business operation and doesn’t completely eliminate humans. The scope of your ERP is limited to those modules (such as Business Intelligence tools, asset management, etc.) that you have opted for.
What is ERP vs CRM?
ERP stands for Enterprise Resource Planning which is a tool that empowers your business with deep analytical insights, predictive analytics, and strategic decision-making. In contrast, CRM stands for Customer Relationship Management which is a customer-centric tool that automates lead tracking & management, and improves the effectiveness of your marketing campaigns.
What are the Examples of ERP Systems?
The following are examples of ERP systems:
- Sage X3: A highly flexible, scalable, and industry-leading solution that supports a wide range of business functions.
- SAP: A solution tailored for businesses of all sizes and industries with amazing integration capabilities.
- Microsoft Dynamics 365: Enhance productivity & performance and provide superior customer service.
- Oracle NetSuite: A unified solution with a user-friendly interface and widespread adoption.
What are the top 10 ERP facts?
The following are the top 10 ERP facts:
1.Integration: Integrate your ERP across different business processes and access through a single unified system.
2.Cloud Storage: Host your data in the cloud for remote accessibility and easier collaboration.
3.Productivity Boost: Reduce potential for human errors, and improve the speed & performance.
4.Inter-departmental Collaboration: Collaborate smoothly across different departments for better efficiency.
5.Visibility: Gain real-time visibility into organization-wide activities for better decision-making.
6.Long-term Cost Savings: Align your resources efficiently and meet your long-term cost-saving goals.
7.Inventory Optimization: Reduce your inventory storage & handling costs, minimize waste, and gain efficiency.
8.Scalability: Get scalability benefits for growing organizations.
9.Customer Excellence: Improve your order processing time and bring standardization across different processes.
10.End-to-end Compliance: Track, manage, and document your compliance activities.
Schedule Product Tour
"*" indicates required fields