ERP vs CRM
Understanding ERP vs CRM difference will help you meet your strategic business needs, enhance operational efficiency, and improve your Return on Investment

What is ERP?
Enterprise Resource Planning is a complete suite of business-specific modules that provides a sweeping overview of your business operations and aids decision-makers with powerful analytical tools and algorithms required for fast & efficient decision-making.
ERP software is increasingly used across companies of all sizes and types. According to the data published by Global News Wire, the EPR market size was estimated to be $63.33 Billion in 2022. It is expected to reach $187.79 Billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 14.8%.
What is CRM?
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) is a system that enables businesses to track, and nurture relationships between business clients, consolidates sales data & communications into one single platform, and provides a multitude of other features for effective sales tracking, shortening the sales cycle, and building effective marketing strategies.
The purpose of using a CRM System is to simplify lead management and improve the performance of sales and marketing campaigns. It is often used in conjunction with other systems such as VoIP telephone calling service for real-time tracking and collaboration.
ERP vs CRM: Know the Difference
Now, let’s discuss the actual difference between ERP and CRM:
| Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) | Customer Relationship Management (CRM) | |
| Definition | ERP is a specialized software that streamlines core business activities from procurement, inventory management, customer relationship management, supply chain, and sales to finance. | CRM is a dedicated tool that streamlines various operations in sales management, including lead management, and sales tracking, among others. |
| Scope | ERP is company-wide, extensive, and encompasses a wider range of business activities, which is why it is also called Business Management Software. | CRM is limited to customer support, lead management, and sales & marketing operations only. |
| Availability | Most ERPs include the CRM functionality. There’s no need to buy it separately. | CRM is a sub-set that does not include many of the business-critical features that are available in an ERP. |
| Objective | The aim of ERP deployment is to enhance customer experience, improve leads, close sales faster, reduce costs, foster growth, enhance operational efficiency, and maximize profits. | The aim of CRM is to turn potential customers into customers and assist with lead management. |
| Core Features |
|
|
| Budget | Expensive | Budget-friendly |
| Implementation Complexities | Deploying an ERP can be a time-consuming, yet highly-rewarding, procedure. | Deploying CRM is relatively simple with fewer complexities. |
| Data Migration & Conversion | Time-consuming | Simple and quick |
| Examples | Examples include Sage X3, NetSuite, AcTouch, Scoro, etc. | Examples include Sage CRM, Zoho, HubSpot, Salesforce, etc. |
| Usage | It is mostly used in medium to large-sized enterprises | It is mostly used in small enterprises with limited budget |
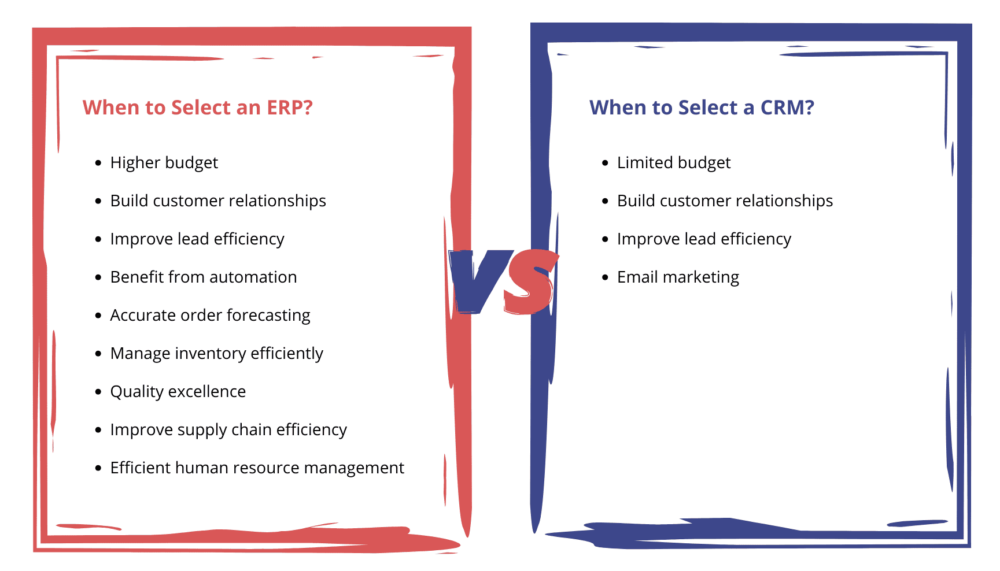
How to Choose Between an ERP and a CRM?
- ERP Tool: If you’re looking for a sophisticated tool with a host of ERP modules that encompass a broader range of activities, your best bet is an ERP. It supports everything from customer relationship management, leads management, sales, production, inventory management, quality control, and supply chain to finance. A survey conducted by Edu Cause revealed that over 77% of the participating companies said the most critical success factor for their ERP implementation was institutional leadership.
- CRM Tool: If you’re looking for a cost-efficient legacy tool that solely focuses on building positive relationships with your customers and managing & improving lead efficiency, go with a CRM. Using a CRM, you will be in a better position to automate key tasks in the leads and marketing management and maintain consistency throughout communication with your existing and potential customers.
5 Best Practices for Successful Integration Between ERP and CRM
→Define Implementation Goals
Define the goal and ultimate objective of the ERP implementation. It can be anything like achieving greater coordination between different teams, improving efficiency, and meeting your sales targets.
→Select an Implementation type
Choose a type of implementation that suits your unique business and industry needs. For example, large enterprises may want to choose phased roll-out to avoid sudden disruptions.
→Data Cleaning
Ensure you are feeding clean and filtered data into the ERP. Preventing data silos and inconsistencies is important to generate highly accurate results for better decision-making.
→Consult with All Stakeholders
Ensure you discuss the goal of your implementation with all the stakeholders involved, viz. business executives, employees, suppliers, and so on. A better coordination between all stakeholders will help you achieve the intended goal of the ERP adoption.
→Develop Implementation Roadmap
Develop a detailed roadmap of implementation. Set clear timeframes, allocate resources, and plan about contingencies & potential technical problems that you may face. A robust implementation roadmap will help you avoid delays, reduce potential downtimes, and achieve results faster.
Maximize Your Business Potential with Sage X3
Sales, marketing, and customer support form the crucial trio of any company’s growth & success. Both ERP and CRM play a vital role in the company’s advancement. However, choosing the right solution is important to ensure that it aligns with your strategic business goals and you will be in an effective position to tackle different industry-specific challenges. Thanks to the plethora of modules that ERP offers, you will always gain an advantage over a CRM.
Sage X3 is a business-critical solution that provides end-to-end visibility into sales, lead management & customer support. It lets you manage sales more effectively, reduce delays in order fulfillment, and find new opportunities for up-selling & cross-selling. It is a one-stop solution that promotes the smooth flow of information throughout the order fulfillment process and enhances coordination among different units.
Top Industries Leveraging ERP Software
Food & Beverage
Alcohol
Pharmaceuticals
Advertising
IT Services
Furniture
Manufacturing
Auto Ancillary
Pharma Trading
Packaging
Medical Device
Chemical
Plastic
Brewery
Logistics
Automotive
Top ERP Articles
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Is CRM Included in the ERP?
Your ERP Application acts as a single and multi-functional solution. It supports different business activities, including Customer Relationship Management. The CRM module is included with most ERPs. However, it may be unavailable if your company has chosen not to opt for it (for example -due to a tight budget) during the billing and payment terms.
Can an ERP Replace the CRM?
Yes, an ERP can replace the CRM. This is because it encompasses all the functionalities that are already included in your stand-alone CRM tool in addition to very highly specialized and customizable solutions that you may want to try out to nurture growth & promote efficiency. An ERP delivers a comprehensive 360-degree overview of your customer information. It lets you track order history & customer information, create sales prospects, and understand the effectiveness of your marketing campaigns.
Can I Use Both ERP & CRM Simultaneously?
Technically, it’s possible to use both ERP and CRM together. However, it can lead to multiple challenges given below:
- Separate Datasets: You will have two separate datasets for the same customer list. This can result in confusion, errors, and productivity loss.
- Additional Costs: Using both tools simultaneously can result in additional costs. Since ERP already has an in-house CRM, there is no need to purchase a separate CRM tool.
- Technical Complexities: It’s possible that your ERP and CRM store their data in two different formats. Integrating such huge data can be a challenging task.
- Employee Training: You will need to train your employees to handle both systems simultaneously, which can overburden your employees.
- Data Security: With two separate datasets, there is an increased risk of data breaches that can lead to severe financial losses, reputational damage, and regulatory penalties.
Who Benefits the Most from Using an ERP?
There are different advantages of ERP over CRM. Consider using an ERP if you want to make use of cutting-edge technology and benefit from centralization and standardization of the data, eliminate labor work, improve organizational productivity & regulatory compliance, and lower operational and administrative costs.
Even though the upfront ERP cost may appear to be higher, investing in ERP is a long-term investment that pays off in the near future. Nevertheless, there are better options such as Cloud ERP with no upfront costs.
Manufacturers across the world use Manufacturing ERP Software to gain visibility into the manufacturing processes and make timely & data-driven decisions.
Pharmaceutical companies use Pharma ERP Software to enhance regulatory compliance, supply chain, and accuracy in day-to-day operations.
Chemical manufacturers use ERP for Chemical Industry to maintain high-quality standards, maintain safety, and adhere to strict regulatory practices.
Food companies use the ERP for Food Industry to manage recipes, manage supplier performance, and quickly fulfill customer orders.
Furniture manufacturers use the ERP for Furniture Manufacturing to track customer orders and build a robust system of supply chain.
Who Benefits the Most from Using a CRM?
As we’ve seen in the difference between ERP and CRM, CRM software enables businesses to benefit from improved efficiency in the sales, marketing, and customer support operations. Use the CRM if you want to enhance marketing efficiency, track the performance of your marketing campaigns, automatically generate Invoices and quotations using an Invoice Management System, and optimize the sales lifecycle.
Another reason why some companies choose a CRM despite the tremendous benefits of ERP is that it saves costs. The ERP implementation is often costly, due to higher upfront costs. The CRM software, on the other hand, is priced cheaper due to the absence of various features such as production, inventory, warehouse, supply chain, and financial management.
How Much Does ERP and CRM Cost?
Best ERP Software in India is costlier than CRMs because of the large feature set it offers. Typically, ERPs cost between $100,000 to $700,000 for medium-sized businesses, whereas CRM costs between $10 to $300 per user charged monthly. The actual product prices may vary from product to product, and modules selected.
What is an example of ERP?
Sage X3 is a popular example of ERP. It is an all-encompassing solution that comes with a robust range of capabilities and industry-specific featureset to gain agility and improve competitiveness. Businesses across different industries and sizes use it to tackle modern-day business challenges, cut costs, and improve efficiency.
What is an example of CRM?
Sage CRM software is a popular example of CRM. It provides accurate project overviews, business profitability analysis, expense & time tracking, and lead sourcing & generation capabilities to convert your potential leads into actual sales.
Schedule Product Tour
"*" indicates required fields