What is Inventory Turnover Ratio?
The Inventory Turnover Ratio is an important metric used in inventory management that measures the number of times a company sells and replaces its inventory within a given duration. It is also known as Stock Turnover Ratio.
Companies across the world use an ERP Software to gain real-time visibility into the inventory levels, improve their Inventory Turnover Ratio, and better manage their inventory without over-stocking or stockouts.
Example of Inventory Turnover Ratio
Let us better understand the inventory turnover ratio with a simple example. ABC Ltd is an Indian company that manufactures electronic gadgets. It had an annual Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) of Rs 1,000,000 and the Average Inventory for the same period was Rs 200,000.
According to our Inventory Turnover Ratio formula, the ratio would be 5 (1,000,000 ÷ 200,000). It implies that the company turns over its inventory five times within a year. A higher ratio in the Inventory Turnover Ratio formula generally indicates more efficient inventory management, suggesting potential for increased sales and profitability. It’s a crucial metric for evaluating a company’s operational efficiency, much like using Financial Management Software.
Inventory Turnover Ratio Formula
Here is the simple formula for calculating the Inventory Turnover Ratio:
Inventory Turnover Ratio = Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) / Average Inventory
Here are the components of the Inventory Turnover Ratio formula:
1. Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
The first component of the Inventory Turnover Ratio formula is the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS). It is the total cost incurred for manufacturing and selling the goods. It includes various expenditures such as the direct labor, packaging expenditure, and commissions paid to sales employees. It is mainly used for setting optimum product pricing, and reducing the company’s tax liability.
2. Average Inventory
The second component in the Inventory Turnover Ratio formula is your average inventory, which indicates how much inventory a business has over a certain period of time. It is mainly used for inventory planning & forecasting, optimizing stock levels, identifying demand trends, and reducing the company’s inventory carrying costs.
Average Inventory = Inventory in the Beginning + Inventory in the Ending Period / 2
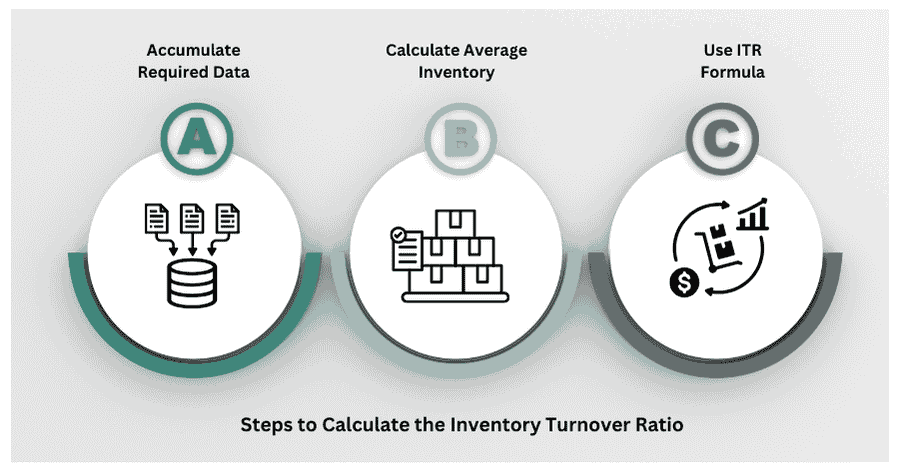
What are the Steps to Calculate the Inventory Turnover Ratio?
1. Accumulate Required Data
First things first, accumulate different data such as the inventory balance and the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) as per our discussed Inventory Turnover Ratio formula. Look for the inventory balance at the beginning and ending of the financial year in your Balance Sheet. The COGS is mentioned under the Expense head in the Income Statement.
2. Calculate Average Inventory
You can calculate the Average Inventory by calculating the total of the inventory balance at the beginning and ending period, and dividing it by two. That’s the second step of our Inventory Turnover Ratio formula.
3. Use ITR Formula
You can calculate the ratio using the Inventory Turnover Ratio formula. Just divide the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) by the Average Inventory. That’s it, the Inventory Turnover Ratio formula is simple and straightforward.
Which is Considered a Good Stock Turnover Ratio?
Typically, a higher turnover ratio is preferred as it indicates increasing demand for the product and higher sales. In contrast, a lower turnover ratio typically indicates lower demand for the product and weak sales.
However, much like any other thing, there are also exceptions. For example, sellers of luxury furniture who use an ERP for Furniture Manufacturing might notice a lower inventory turnover as the demand for such high-end products may be limited.
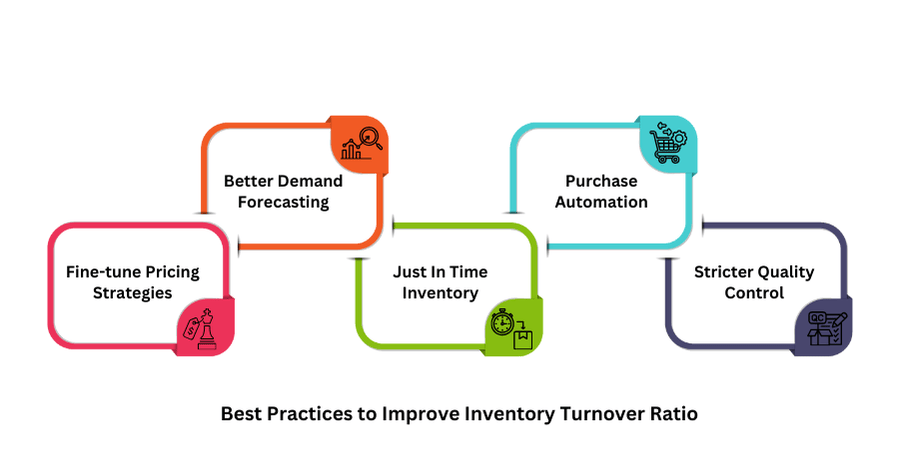
Best Practices to Improve Your Inventory Turnover
1. Fine-tune Pricing Strategies
The pricing of your products plays an important role in driving or shrinking their sales. If you’ve a significant stock of obsolete inventory, it may increase your storage costs. Deploying a Sales Management System can help you prevent future occurrences. Think of selling it off through aggressive promotional, discounting, and marketing campaigns. For example, offering the obsolete inventory at an amazingly lower price, or bundling it with your regular products.
2. Better Demand Forecasting
The primary objective of Demand Forecasting is to anticipate the future demand for your products and maintain consistent availability. Your Inventory Turnover may be low due to poor planning and research, leading to significant obsolete stock. Utilize Business Intelligence Tools that capture your sales data in real-time, enhance forecasting accuracy, and help you grab new opportunities. This will help you improve the outcomes of the Inventory Turnover Ratio formula.
3. Improve Supply Chain Efficiency
One way to improve your Inventory Turnover Ratio formula is to optimize your supply chain operations through the deployment of state-of-the-art technologies such as Supply Chain Management Tools. Building an efficient supply chain network, automating labor-intensive processes, and improving the order fulfillment rate can not just improve the turnover ratio but also increase your profit margins.
4. Just In Time Inventory
Merely relying on the Inventory Turnover Ratio formula won’t be enough. The Just In Time method of inventory management keeps minimal inventory on hand by aligning your raw material procurement with the actual production schedules. A dedicated Inventory Management System can be helpful.
5. Purchase Automation
A Procurement Software will help you streamline the entire procurement process and improve the accuracy level. By ordering the right quantities of products at the right time from the right supplier, you can minimize the instances of inventory obsolescence, improve the Inventory Turnover Ratio, and lower your stock holding costs.
6. Stricter Quality Control
Increasing instances of order returns and replacements can contribute to stock obsolescence, leading to poor outcomes in the Inventory Turnover Ratio formula. Monitor your production process, set clear quality standards, and conduct regular testing at every level. You may also want to train your employees and procure raw materials from quality vendors.
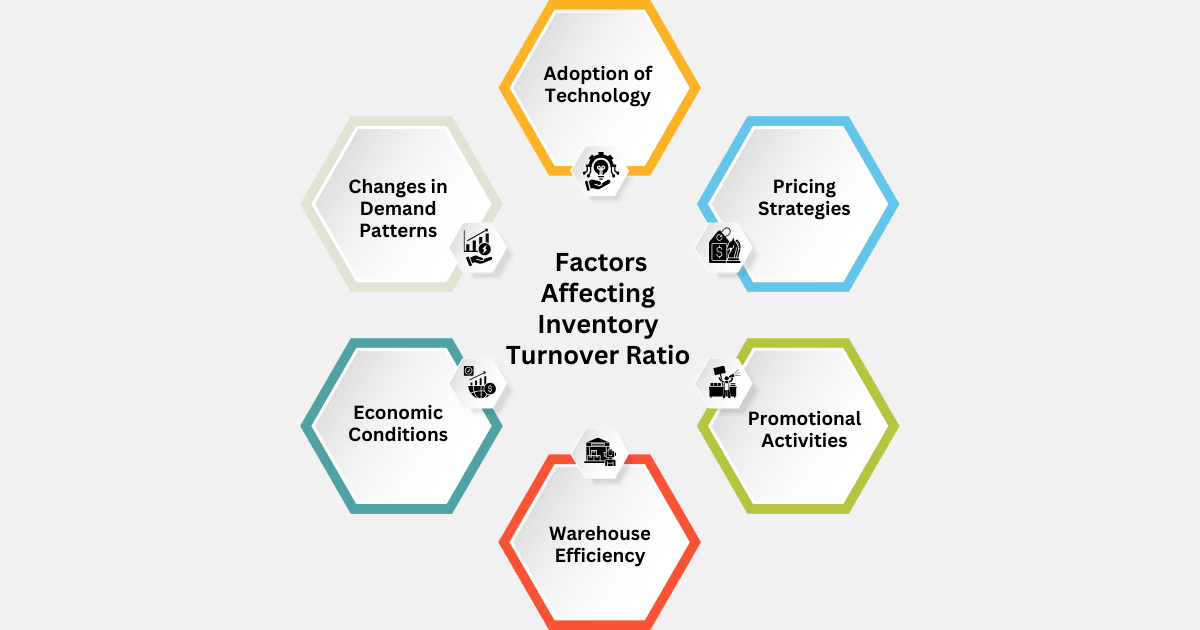
Which Factors Affect the Stock Turnover Ratio?
1. Changes in Demand Patterns
Sudden spikes or drops in the demand for your products can impact your Inventory Turnover. Excessive availability or scarcity of products, seasonal fluctuations, and supply chain disruptions, can contribute to such spikes or drops. You can track such changes using a Cloud ERP.
2. Adoption of Technology
Businesses that adopt modern technologies such as ERP Application benefit from greater inventory efficiency, and higher inventory turnover. In contrast, businesses that rely on manual tracking of inventory, may experience slower turnover speed.
3. Pricing Strategies
Another factor that affects the outcomes of the Inventory Turnover Ratio formula is the pricing strategies adopted by the management. For example, increasing the product pricing would lead to less inventory turnover, and vice versa.
4. Promotional Activities
Promotional activities such as free samples distribution, product demonstrations, promotional discounts, loyalty programs, and different branding activities, can increase or decrease the inventory turnover.
5. Warehouse Efficiency
Inadequate warehouse storage and other warehouse-specific problems can lead to slower movement of inventory and lower inventory turnover. In contrast, businesses with efficient warehouse facilities and a Warehouse Management System in place, can sell and restock their stock quickly, leading to better inventory turnover.
6. Economic Conditions
Economic down-times or booms can cause changes in wages, consumer confidence, and disposable income, ultimately leading to fluctuations in the demand patterns. As the demand curve shifts from the left to the right, business may experience variations in the turnover ratio.
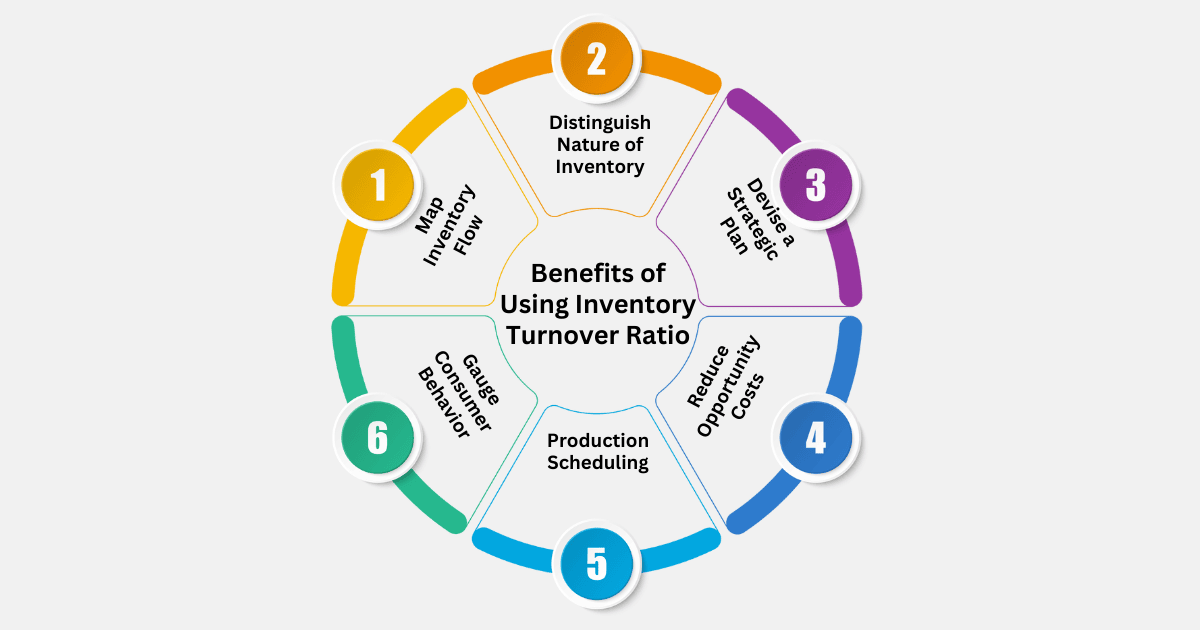
Benefits of Using the Inventory Turnover Ratio
1. Map Inventory Flow
Using an Inventory Turnover Ratio calculator alongside ERP implementation will help you understand which products are saleable and which ones are not. Accordingly, you can take appropriate measures to reduce the inventory storage costs, and minimize the instances of stock-outs.
2. Distinguish Nature of Inventory
Regularly calculating the Inventory Turnover Ratio formula allows you to distinguish the nature of the inventory, viz. short-term or long-term. Short-term inventory includes all the fast-moving goods such as groceries, retail clothing, and electronics that have a higher turnover. In contrast, long-term inventory includes goods with lower turnover, such as heavy machinery & luxury goods.
3. Devise a Strategic Plan
Some products are evergreen as they can be sold throughout the year, whereas other products can only be sold during a specific interval (such as rainy season). With an effective inventory plan in place, you can devise a strategic plan for discounting and disposing of your stock.
4. Reduce Opportunity Costs
An Opportunity Cost is the potential loss of revenue from missed sales opportunities. Many Indian food companies deploy an ERP for Food Industry to analyze their inventory turnover and understand how well they have been doing. This helps them take measures to control their opportunity costs.
5. Production Scheduling
Effective production scheduling is possible when a strategic inventory plan is in place. By analyzing your turnover ratio and deploying Business Intelligence Tools, you will be able to prevent over-stocking and under-stocking, and efficiently schedule the production activity.
6. Gauge Consumer Behavior
Performing extensive analysis of your inventory and its disposal pattern will allow you to gauge the consumer behavior, and the demand for your products. Let’s take an example of furniture companies that deploy ERP for furniture monitoring to gauge the consumer interest before fully stocking their inventory.
Limitations in the Usage of Inventory Turnover Ratio
1. Seasonal Demand Patterns
The demand for some products, such as an umbrella, is led by seasons. Sales for such products may drop in non-seasons despite taking extensive measures.
2. Industry-wise Comparisons
The ratio differs from industry to industry. Some industries may have a higher ratio while others may have a lower ratio.
3. Inventory Tracking Errors
Some businesses still rely on manual inventory tracking. Errors in the inventory tracking can lead to incorrect Inventory Turnover Ratio calculator findings.
4. High-value Products
As we’ve discussed in the Inventory Turnover Ratio meaning section, high-value products have a lower inventory turnover as these items move off the shelves at a lower speed compared to low-value products.
Wrap Up
Inventory Turnover Ratio is an important metric used by modern-day businesses to visualize the flow of their inventory, maintain an optimum inventory count, and take various measures for cost reduction & inventory optimization.
Sage X3 is a business-critical software that empowers your business with robust analytical capabilities, inventory planning, forecasting, and optimization. It offers a plethora of features that can significantly reduce the labor-intensive activities and expedite your order fulfilment.
FAQs
1. How to Define Inventory Turnover Ratio in Simple Words?
The Inventory Turnover Ratio meaning in simple words, means the number of times a business sells and replaces its stock of inventory within a specific duration of time. It is used by businesses across all sizes and types for better inventory planning & forecasting, and financial decision-making.
2. What is the Ideal Stock Turnover Ratio?
The ideal ratio of Inventory Turnover can be between 5 and 10. However, as we’ve already discussed in the what is Inventory Turnover Ratio section, it can be higher for companies selling perishable items (such as milk, fruit, vegetables, yogurt, egg, etc.,). Such companies may need to sell their products faster to reduce the instances of spoilage or wastage.
3. What is Considered a Bad Stock Turnover Ratio?
A turnover ratio that is lower than the industry average is typically considered unfavorable. It may indicate your sales strategy is not driving expected results, and a significant business capital is stuck in unsold inventory. Ultimately, it may result in higher increased inventory costs, and a risk of product obsolescence.
4. How to Fix a Low Stock Turnover Ratio?
There is no one-size-fits-all solution that works for every company across all industries. You will need to identify and address the root cause. For example, use an Inventory Turnover Ratio calculator, look for the pricing strategies of your competitors, changes in consumer behavior, and current demand patterns. You may also want to fine-tune your marketing strategies and get rid of inefficiencies with the Best ERP Software in India.
5. What Does an Excessively Higher Stock Turnover Ratio Indicate?
A turnover ratio that is too high may indicate a potential problem in the company’s inventory handling. For example, your Inventory Turnover Ratio calculator may indicate that the company is selling its inventory too quickly and risks running out of stock. It may not be in a position to fulfil the market demand and end up losing significant sales opportunities & dissatisfying its consumer base.
6. How Does Stock Turnover Ratio Affect Financial Modeling?
The outcomes of your Inventory Turnover Ratio calculator play an important role in a company’s financial modelling and significantly affect its various financial metrics. It helps companies get key insights into their performance in inventory handling, and develop unique strategies to lower their inventory handling & storage costs, and minimize wastage.
7. Is Stock Turnover Ratio Mentioned Anywhere in the Balance Sheet?
No, the Inventory Turnover Ratio is not mentioned anywhere in the Balance Sheet, Income Statement or other financial statements. As we’ve define Inventory Turnover Ratio earlier, you will need to manually calculate it based on the different figures available in the Balance Sheet. These figures are the stock at the beginning and ending of the financial year, and your annual sales.