What is Journal Entries?
Journal Entries are the building blocks of the double-entry accounting system, which contain a concise record of your business transactions in chronological order, and reflect their individualistic impact on your company’s books of accounts.
Journal Entries are rightly called the backbone of the modern accounting system as they are the first-hand records of any transaction in your business and form the basis of the financial statements prepared at the end of the accounting period.
Which Information is Included in Journal Entries?
Now that we’ve discussed what is Journal Entries, let us understand which information is stored in them as per the accounting standards.
- Header Information: This contains a brief description of the entry type and the date of the business transaction.
- Reference Number: This contains a numerical reference number of the corresponding business transaction.
- Debit Entries: This contains the actual business transactions that will be debited from the financial statements.
- Credit Entries: This contains the actual business transactions that will be credited into the books of accounts.
- Transaction Description: This contains a short description of the corresponding transaction for future reference.
Different Types of Journal Entries
Businesses have to record the following types of journal entries:
| Journal Entry | Usage |
| Opening Entries | Beginning of the accounting period |
| Transfer Entries | Transferring an amount within the same entity |
| Closing Entries | End of the accounting period |
| Adjusting Entries | Correcting omissions & human errors |
| Compound Entries | Transaction contains multiple Debit & Credit entries |
| Reversing Entries | Reversing the effects of Adjusting Entries |
1. Opening Entries
This accounting type maintains continuation by recording the ending balance of the previous period as the beginning balance of the current period. For example, suppose the previous closing balance under the cash account on the balance sheet was ₹1,00,000. This amount will become the opening entry of the next journal.
2. Transfer Entries
Transfer entries record transactions about moving or allocating expenses or incomes from one account to another. For instance, Company ABC made a payment to its subsidiary. The transaction will be recorded under a transaction entry in the journal.
3. Closing Entries
The closing entry is the amount mentioned at the end of the journal. Initially, the closing entry is noted in a temporary account before being moved to a permanent account, and the value of the temporary account becomes zero. Expense and loss, income or gain, income statement, dividends, or withdrawal account are some examples of temporary entries.
4. Adjusting Entries
All transactions recorded following the accrual method of accounting get recorded in the adjusting entries. They help maintain transparency in the reporting system by recording entries that otherwise are not accounted for. Accruals, deferrals, and estimates are some examples of adjusting entries.
5. Compound Entries
Some transactions involve debiting or crediting multiple accounts. They are recorded under compounding entries. The bookkeeping rules require the final value of the debit and credit sides to be equal. However, there is no restriction on the number of entries on either side. Hence, one can make multiple debit entries against one credit entry or vice-versa if the value remains unchanged.
6. Reversing Entries
A reversing entry marks the first entry into a journal made to reverse, undo, or adjust any transaction made in the previous year. These entries eliminate the chances of any error in the accounting system and improve the transparency and efficiency of the process.
Journal Entry Example
While compiling the books of accounts at the end of the accounting period, a business employs either a double-entry or single-entry bookkeeping system. Nowadays, these processes are streamlined using ERP implementation.
Example 1: Purchase of Machinery
XYZ Ltd purchases machinery worth Rs. 10,00,000. The company makes the entire payment in cash.
Here is the journal entry example of XYZ Ltd:
- Debit the Machinery account for Rs. 10,00,000
- Credit the Cash account for Rs. 10,00,000
In the above example, as machinery is considered a capital asset, there is no immediate expense journal entry. However, expense journal entry. However, as the machine wears and tears over some time, the company will record expense journal entry for calculating depreciation expenses.
Example 2: Capital Expenditure
Another company, ABC Ltd, acquires land worth Rs. 10,00,000, and buildings worth Rs. 200,00,000. The company paid Rs. 5,00,000 in cash and signed a credit note for the unpaid amount.
Here is the journal entry example of ABC Ltd:
- Debit the Land account for Rs. 10,00,000
- Debit the Buildings account for Rs. 20,000,000
- Credit the Cash account for Rs. 500,000
- Credit the Notes Payable account for Rs. 20,500,000
In the above example, the company acquired land and buildings which are fixed assets. Thus, they are considered capital expenditures and recorded in the Balance Sheet with no immediate expense journal entry. While the land is not a depreciated property, the building is. Over a period of time, it is recorded as an expense journal entry while calculating its depreciation for wear & tear.
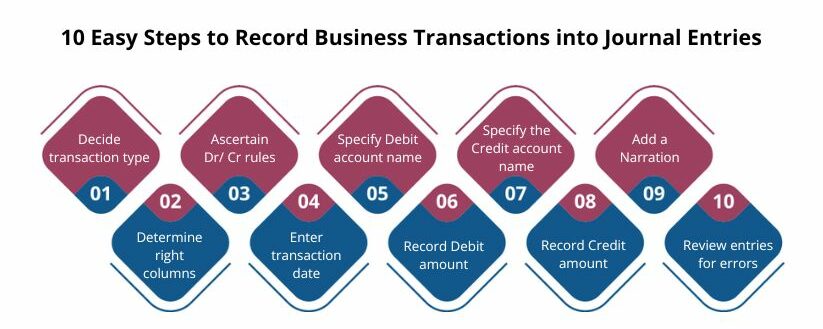
10 Easy Steps to Record Business Transactions into Journal Entries
Your accounting staff needs to go through a series of steps to record business transactions into Journal Entries. The exact steps may differ depending on the nature of the transaction.
- Decide the nature of the transaction, whether debit or credit
- Determine the right columns to record the transaction
- Ascertain the rules of debit or credit that apply to the account
- Label all transactions with a date for future references
- Write the account’s name in the debit column along with ‘Dr.’
- Update the amount on the debit column
- Similarly, identify the account to be credited and write in the next line beginning with ‘To’
- Write the amount in the credit column
- Add a narration at the end of the journal ledger
- Review your entry and ensure you’ve accurately recorded it.
What are the Advantages of Journal Entries?
Journal entries are a crucial part of the company’s books of accounts. They provide the following advantages:
1. Reduce Errors
Journal entries contain detailed information regarding transactions that form the base for the company’s Balance Sheet. Because it contains details, journal ledgers reduce the chances of errors – omissions or incomplete transaction records.
2. Track Financial Implications
It records the breakdown of transactions, helping you maintain accuracy in your accounting process. Journal accounting allows you to track the implications of each debit and credit entry with minimal chance of omissions.
3. Accounting Reference
Other advantages of journal entries include a backup in preparing audit reports and balance sheets. Auditors can refer to the entries or double-check for errors or omissions for details. The detailed nature of a journal helps capture every detail.
4. Extensive Dataset
The journal contains details regarding transactions that function as a reference for accountants and auditors. As a result, you gain deeper financial insights into the company’s operations and can be concise with the other financial reports.
5. Chronological Order
In the journal entry, transactions are recorded as soon as they occur in the chronological order. This date-wise recording helps businesses better understand where their money goes and where their revenue comes from.
What are the Disadvantages of Journal Entries?
While journal entries are an integral part of financial management, there are a few disadvantages of journal entries:
1. Size of Journal
As the size of the business grows, managing all the transaction entries becomes a complex task, and the journal’s size increases, making it difficult for the organization to maintain and record all transactions.
2. Lack of Internal Checks
Usually, one employee maintains all the entries in a journal, making it difficult for internal checking and auditing. Increasing the number of transactions also increases the complexity.
3. Separate Cash Ledger
Another disadvantage arises from maintaining a separate journal, called the cash book, for cash entries. It makes the process of matching and tracking transaction entries cumbersome, increasing the chances of missing information.
4. Accounting Omissions
Another problem with journal entries is that of accounting omissions. Sometimes, accountants may forget to make some journal entries pertaining to incomes and expenditures. Such omissions in the statements of the financial year are recorded as unrecognized incomes and expenditures through Adjusting Entries.
5. Repetitive Transactions
Other disadvantages of journal entries include repetitive transactions. It is a common practice to debit and credit the same accounts for different transactions repeatedly. Not only does it make your journal entry bulky & voluminous, but also increases the accounting complexity.
Final Words
As a business grows in size, so does its accounting complexities. Manual errors creep in, and it becomes difficult to identify & correct them. ERP Software consolidates business data and automates most accounting tasks using its integrated financial modules, thus freeing up your accounting staff for higher-value activities.
Sage X3 is an exceptional solution for modern-day businesses that are looking to leverage innovation & technology to ease accounting complexities. With a single source of information, businesses gain unprecedented visibility in the accounting procedure and avoid compliance penalties. In today’s highly competitive and rapidly changing business environment, it stands out as the golden jewel of your business’s growth & success.
FAQs
1. What is the Definition of Journal Entries?
Journal Entries meaning is that they are the initial records of your business transactions which require both debit and credit to complete each transaction entry. They are later summarized and transferred to the General Ledger.
2. What are Debits & Credits in Journal Entries?
Debits and credits are the two main entries recorded in the accounting journals. The journal entry follows the double-entry bookkeeping method, meaning both debit and credit sides in the journal match.
- Debit: Debit refers to the payments made or owned by the business. Usually, debits are recorded on the left side of the journal.
- Credit: Credit refers to adding a record of the decreasing value of an asset or increasing value of liability. The credit entries are recorded on the right-hand side.
For example, ABC Ltd receives Rs. 50,000 from a customer for the services rendered. As this transaction positively impacts the company’s cash flow in the cash flow statement, it will be debited from the Cash Account and credited to the Accounts Receivable.
3. Why are Journal Entries So Imperative for Businesses?
As per journal entries meaning, journal entry forms the basic or the fundamental of effective and accurate accounting. They give an accurate and detailed description of every transaction. Both internal and external auditors scrutinize journal entries to ensure compliance with the accounting standards. Modern-day businesses are leveraging finance module in ERP to streamline the process of recording journal entries and reduce the risk of errors & non-compliance.
4. How to Record Account Payables in Journals?
Accounts Payable refers to the payment a company owes to its creditors or suppliers. It is an obligation on the part of the company to pay the amount within the stipulated time period. To record the account payables, the business must pass the entries under the debit or the asset account and simultaneously credit the payable account. An ap automation tool helps automate the journal entry process and make the process error-free.
5. What is the Difference Between Double-entry & Single-entry Bookkeeping Systems?
Double-entry bookkeeping is extremely common across the world where journal entries are recorded twice. For example, if a company purchases new machinery worth Rs. 3,00,000, the same amount is debited from the Cash Accounts and credited to the Current Assets section.
In contrast, a Single-entry system is very rarely used. It contains a mere tally of the cash coming in and going out. If a company purchases machinery worth Rs. 3,00,000, the accountant will reduce the same amount from the cash.